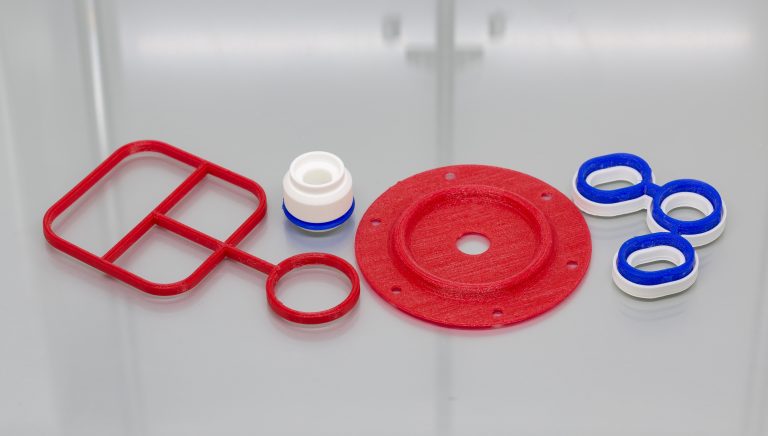
3D printing for seals
3D printing has developed significantly and now performs a crucial role in many applications. 3D printed products vary from fully functional to purely aesthetic applications – commonly for manufacturing. Here we discuss how our engineers use this technology to demonstrate a seal concept.
What is 3D printing?
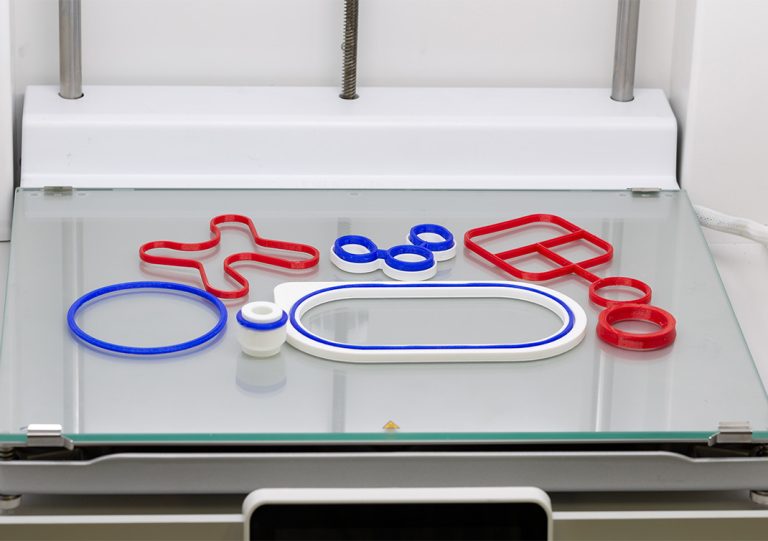
The typically common name for additive manufacturing is 3D printing. The process involves the construction of a three-dimensional shape designed and generated from a computer aided design program (or CAD). The most typical process used for 3D printing is FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) or FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling).
The FDM process uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. It’s then deposited onto the 3D print bed, creating layer by layer, gradually building up the 3D model structure. We commonly use this process to create our design and development range of 3D printed models and seal prototypes.

What material is suitable for 3D printing?

Material compatibility with the process is imperative and a range of thermoplastic grades are used. Typical suitable material grades include; Polylactic acid (PLA), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), Nylon and Polypropylene (PP).
The most common grade we use for 3D printing is PLA – for its great strength and stability. We’ve also adapted our design process to use more TPU based material grades, as it loosely demonstrates the same properties as elastomer grades and is better for using in prototype programmes where mechanical fit in groove is tested.
Why use 3D printing for seals?
3D printing is used for a variety of designs and seal types. From O-rings, gaskets and lip seals – to grommets, multi shot mouldings and large seal assemblies.
Using 3D printing during the initial design stages of a project comes with many benefits. The rapid turnaround means a simple seal design will be produced in around 15 minutes. Additionally, even more complicated parts can be manufactured in the same day. We can even print the application housings – a perfect demonstration to an engineer what they can expect from a seal part. They will see the shape and fit for hardware without the lead time and cost of cutting a prototype tool for moulded parts.
This solution is particularly suitable for quick turnaround gasket designs. For example for automotive applications or similar critical markets. Our engineers can design the concept and then 3D print a rapid prototype of a gasket to suit a 3D printed gauge groove.
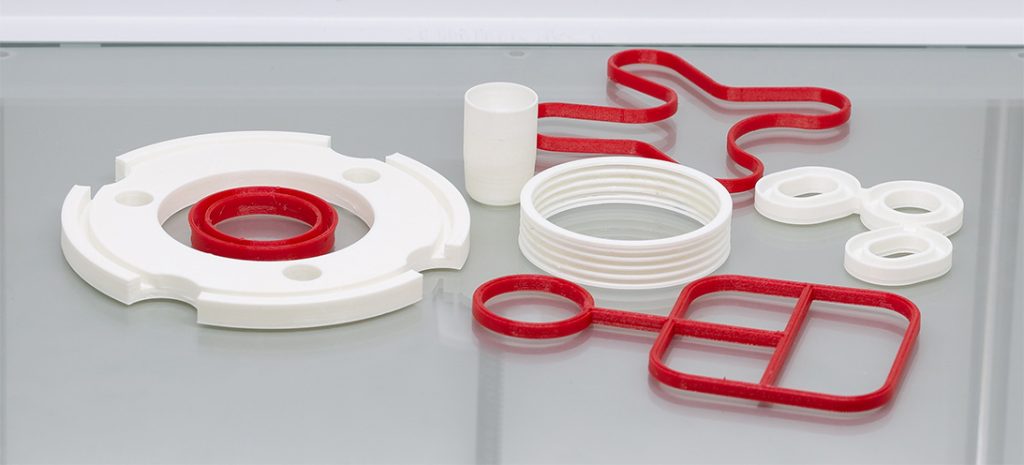

Demonstrating to our customers that the seal has been fit checked for installation, builds further confidence in the design recommendation. Our engineers combine the 3D print with FEA simulation reports to offer a fully engineered sealing solution.
Learn more about our design and simulation service HERE