EPDM
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) is a synthetic terpolymer rubber with a saturated polymethylene backbone, coming under the M-Group of materials.


What is EPDM?
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is a synthetic terpolymer rubber with a saturated polymethylene backbone, coming under the M-Group of materials. Rubbers with a saturated polymer background exhibit better resistance to light, heat, steam and ozone compared to unsaturated types such as NBR. Depending on the specific compound, it can be formulated to use a sulphur curing process (known as cross linking) or a peroxide curing system, with the latter materials generally having better thermal and chemical resistance properties. Sulphur cured EPDM generally have higher tensile and tear strengths, which can be beneficial for certain applications such as gaiters and boots..
When to use EPDM
EPDM is an ideal material choice for many applications exposed to low temperatures, the atmosphere, hot water/steam, CIP/SIP processes or sealing glycol and phosphate ester based fluids. In such cases, similarly priced NBR seals are far less likely to achieve suitable lifetimes in service and whilst there are more material options from the M-Group (notably FKM and FFKM) that can push some capabilities further, the much higher cost of these options may not always be justifiable in the application.
EPDM is a good sealing material for applications exposed to ozone and weathering with excellent aging resistance. It is also suitable for sealing phosphate ester based fluids, which can often cause high swelling in other elastomers, and glycol fluid mixes often found in automotive brake systems. With excellent low temperature flexibility it is a good elastomer choice for cold applications whilst also being particularly resistant to hot water and steam and many chemicals used as cleaning agents in the food, medical and chemical processing industries, such as sodium and potassium hydroxides. Whilst resistant to polar solvents and silicone based oils and greases, contact with mineral based fluids results in severe material breakdown relatively quickly and should be avoided. Generally suitable for temperatures between -45°C (-49oF) and +150°C (302°F), specific grades can achieve -57°C (-70°F) and others can achieve up to +260°C (500°F) for limited periods.
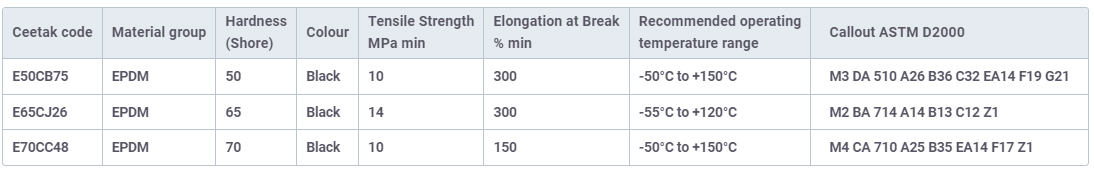
Standard EPDM materials
This is a small selection of our general purpose EPDM materials. Many more compounds are available and can be chosen to suit the specifics of the application.
The tensile strength and elongation are for specification purposes. Typical achieved values can be significantly higher.
Temperature range is general recommendation for static application in air. Temperature ratings are subject to full application review.