Polyacrylate & Ethylene Acrylate Rubber (ACM/AEM)
Polyacrylate (ACM) & Ethylene Acrylate (AEM) consist of polymerised ester and a curing monomer and are M-Group elastomers.


What is ACM/AEM?
ACM (polyacrylate rubber) consists of a polymerised ester and a curing monomer and being an M-Group elastomer has a saturated backbone coupled with polar side groups in the molecular structure. This results in excellent resistance to heat, ozone and hot oils and makes it significantly better than NBR materials. However, resistance to water, acids, alkalis and glycols is poor, whilst low temperature flexibility and physical strength (including resistance to compression set) is only fair. AEM (ethylene acrylate rubber) is a similar material with slightly improved high and low temperature capability, but poorer overall chemical resistance and at an increased cost.
When to use ACM/AEM?
The improved hot oil resistance capability (compared to an NBR material) will often justify the slightly higher cost of an ACM seal. In applications where additives (such as sulfur) are used in the lubricating oils, ACM can be a cost effective solution compared to more expensive M-Group rivals (such as FKM). It can also be preferred over silicone based materials for some hot air applications. If the application is exposed to ozone and the atmosphere, the improved resistance to ageing that ACM offers can give substantial lifetime advantages.
ACM is an ideal choice in the automotive industry for “under bonnet” applications, where the high temperature and hot oil resistance is significantly better than NBR options for a modest increase in cost, and well below the substantial cost increase associated with FKM alternatives. Use within the engine and gearbox lubrication systems is common, whilst water and glycol based fluid resistance is poor and exposure to these fluids should be avoided. General temperature capability is -20°C (-4°F) to +177°C (+350°F) but as with most elastomers special formulations can extend this, and lower temperatures of -35°C (-31°F) can be achieved.
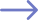
Standard ACM/AEM materials
This is a small selection of our general purpose ACM/AEM materials. Many more compounds are available and can be chosen to suit the specifics of the application.
The tensile strength and elongation are for specification purposes. Typical achieved values can be significantly higher.
Temperature range is general recommendation for static application in air. Temperature ratings are subject to full application review.