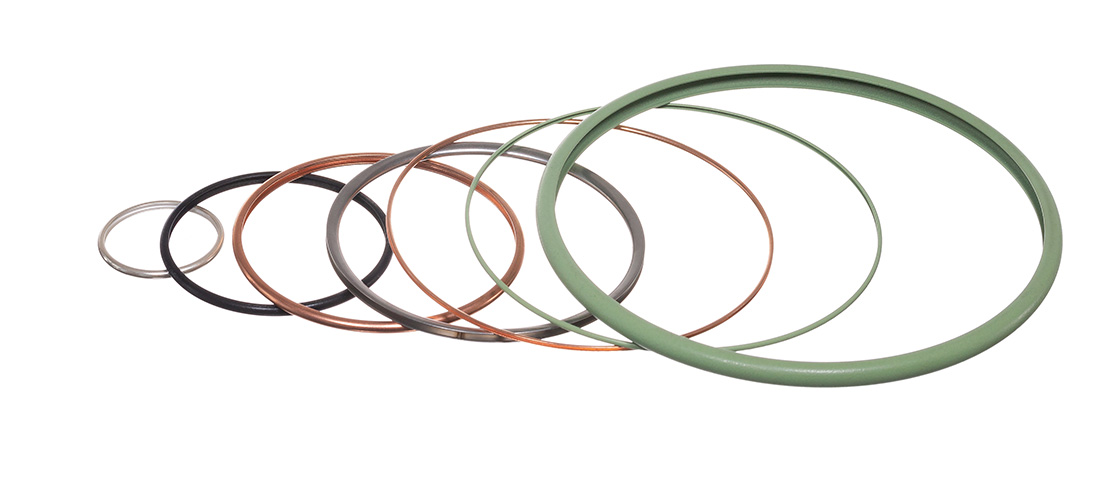
Precision Sealing for Naval Radar Slip RingPrecision Sealing for Naval Radar Slip Ring The application Our customer is a globally recognised leader in the design and manufacture of advanced slip ring systems and contactless rotary joints. Their technology ensures the reliable transmission of power, data, and media across a wide range of rotating interfaces. Read more about how our engineers developed a custom spring-energised seal for this application. The application for this project is as demanding as they come. A naval radar system operating in some of the harshest conditions on the planet.Mounted on a naval vessel, the slip ring assembly must operate continuously. Therefore it needs to function flawlessly, protecting electrical components whilst exposed to the elements (seawater, rain and wide temperature fluctuations). The challenges As well as these demanding conditions, the application itself also had several challenges. Furthermore, the design is a compact seal envelope, meaning design and installation need careful consideration.A durable seal is needed - the expectation is that it can withstand over 6 million cycles across a 10-year service life. The seal required minimal breakout friction to avoid wear and conserve energy consumption.This application required a rotary seal with low temperature capability and excellent resistance to oil-based fuels. The new design will replace the existing seal in the available housing between the rotating metal faces. We concluded a standard spring energised rotary seal would not work in the application, therefore we created a bespoke design. Our sealing solution Our engineers developed a custom spring-energised seal, tailored precisely to the application’s needs. We adapted the Parker Praedifa NLO profile and optimised it with a low-load spring for reduced friction, and a high-performance material formulation offering exceptional wear resistance.Additionally, we included a design feature - heel slots allowing for dowel pin integration within the hardware to provide enhanced application stability. Results The final design delivered excellent sealing performance, passed all endurance tests, and met the full 10-year lifecycle requirement. Consequently, it maintained low friction throughout, ensuring energy efficiency and minimal wear. This is exactly what’s needed for a radar system where reliability is non-negotiable.Learn more about our rotary seals HERE.

Precision Sealing for Naval Radar Slip Ring 
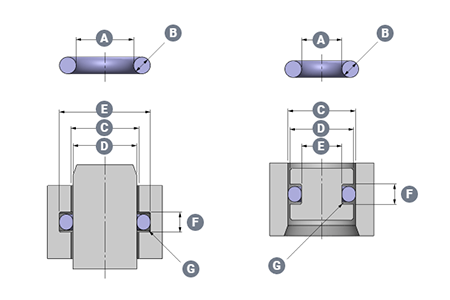
Surface finish requirements for static and dynamic sealingWhat is hardware surface finish?
Any surface can look (and even feel) perfectly smooth. However, look closely enough with high magnification and all surfaces will have a degree of fluctuation. The topography will look similar to a mountain range or the surface of the moon! The way a surface is produced or machined, along with any subsequent processes such as coating or plating, often determines its roughness. Just a couple of decades ago, the standard approach to assessing surface finish was to use comparison plates. These small specimen sections were made by turning, grinding, or milling the material. Inspectors would then run a fingernail across the finished part and the plates to determine which one matched most closely.
What is Ra?
Historically, seal catalogues typically recommended a surface finish using just the Ra (metric) or CLA (Centre Line Average, inches) parameter. Little regard was given to what the seal was being expected to do. Ra simply, is the mean roughness. The average calculated from the peak heights and valley depths. A surface that is mostly spiked can have the same Ra value as one that is mostly troughed. However, each could have a very different impact on seal performance. Today, surface finish measuring equipment is more sophisticated. It’s capable of tracing a surface finish using a diamond tipped stylus, or non-contact 3D laser scanning. These devices are now reasonably affordable and provide a sophisticated level of results from essentially a portable machine. Consequently, these instruments can now analyse the surface roughness profile, trace, also calculate a large range of parameters that define that profile. This includes Ra, Rt, Rz, Rmax, Rmr (bearing ratio) and even skewness parameters. What these are, and how they should be measured, have generally been well captured in standards. These standards include ASME B46.1, ISO 4287, ISO 4288 and the upcoming ISO 21920.
Why is surface finish important for sealing systems?
To ensure seal effectiveness, a common assumption for specifying a hardware surface finish is the smoother the finish the better. However, this is not always the case. If the seal application is static and is sealing a low molecular size gas such as helium; then a very smooth surface would be preferable. This is often referred to as a “closed” surface (with no peaks and very few, shallow valleys). The seal mates tightly against the hardware, ensuring the leak path for the gas is reduced as much as possible. Even in this scenario, the required surface roughness can be influenced by other factors. These include the hardness (or rather, softness) of the seal material and the pressure being applied, both by the initial seal squeeze and the applied gas pressure. It’s important the interface between the seal and the hardware is well lubricated. This is critical for some dynamic applications for either seal friction (and hence noise, vibration and heat) or wear life. This is partly achieved by ensuring that the surface is more “open”, with small valleys or troughs to trap the lubricant -but no sharp peaks that would abrade the seal material. In these application cases, if the dynamic hardware surface (rod, shaft or piston bore) is too smooth, then the seal can wear prematurely. This can cause juddering, squeal and excessive heat build-up.
Tribological performance consideration
As a result, for dynamic applications it is important to consider all the factors affecting the tribological performance. These include the seal (design, material), the dynamic hardware (hardness, material type) and the fluid (viscosity, lubricity, contamination). The hardness of the dynamic hardware can also be a significant factor. Hardened or chromed steels around the 50 Rockwell C level or less can often be polished by the seal itself. Therefore, even if the initial roughness is sub-optimal, good sealing performance is achieved after a brief period of bedding in. With the use of high hardness coatings such as HVOF and DLCs, the much softer seal material is very likely to be abraded by the hardware. In these cases, it’s essential to ensure that the optimal surface finish is met. This often requires a finer finish prior to the coating process. This is because coatings can be rougher than the substrate material, and post-process polishing is challenging with such hard coatings.
Any other factors to consider?
Yes! Another thing to consider is the direction (or lay) of a particular surface finish. Machining marks, scratches, dents or other hardware damage that cut across a sealing contact face are likely to result in leakage. This is compared to (for example) concentric machining marks in the base of an axial face-seal O-ring groove. It is important to consider specifying a lay direction when applying surface finish requirements to the hardware design specifications and drawings. What hardware surface finish should you specify?
Despite complexities involved in hardware surface topography, the sealing industry has developed a comprehensive set of recommendations. These can vary a little between different manufacturers and suppliers. Given the specificity of the seal design and material, they’re best found within the specific literature for the products considered for the application. This is a good starting point, but for each individual application it’s worth considering whether these specifications should be addressed. For example, specifications could be tightened, or perhaps even loosened to ensure that performance targets can be met. This would reduce the need to over-specify the surface finish – because this can add unnecessary processing cost to a part. The practicalities involved in accessing the surface to measure also need consideration. It’s notoriously difficult to check the sidewalls of an O-ring groove, especially in a rod/ID sealing configuration. Cylinder bores are often less tightly defined due to stylus/probe access issues compared to rods and shafts. Importantly, anyone producing and checking a particular surface finish must have both the equipment and the understanding to do so. This is very important if using relatively modern and less well known parameters such as Rmr (or Tp, bearing ratio). Further detail can also be found in the ISO and ASME standards regarding measuring settings. For example, filtering/cut-off values, stylus tip radius, measuring, evaluation and tracing lengths. When validating a supplier’s measurements, it’s important these machine settings are identical. Failure to do so will result in differing surface finish values obtained on the same part. Those standards are not specific to sealing applications. Generally, we’d recommend a cut-off filter (λc) of 0.8, unless measuring very fine (< 0.1 µm Ra) surface finishes where 0.25 would be more suitable, with a 2 micron stylus tip in all cases.
Engineering expertise
Specifying the right surface finish for the hardware components that contact a seal can be complex and daunting. We will ensure an optimum finish and right-first-time seal performance. This is with our core understanding, and consideration of relevant parameters for the given application. For more on our engineering expertise, read HERE

Surface finish requirements for static and dynamic sealing 
Using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) in seal designUsing Finite Element Analysis (FEA) in seal design Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a computerised modelling method for predicting how an object reacts to forces, whether directly applied or generated by pressure, temperature effects or vibration. FEA provides data to help predict how a product will function under those applied conditions. Additionally, it identifies areas where the design can be optimised and improved, without having to test multiple prototypes.Our specialist software uses mathematical models to understand and quantify the effects of real-world conditions on a part or assembly. It can be used to identify potential causes where sub-optimal sealing performance has been witnessed and can also be used to guide the design of surrounding parts. Importantly for products such as diaphragms and boots where contact with adjacent parts may need to be avoided. The software also allows force data to be extracted . For example, compressive forces for static seals and friction forces for dynamic seals can be accurately predicted to help our customers in the final design of their products. Why do we use Finite Element Analysis (FEA)? Our engineers encounter many sealing applications that are critical and have many complicating influences. Envelope size, housing limitations, shaft speeds, pressure/temperature ratings and chemical media are all application parameters that our engineers must consider when designing a seal.In isolation, the impact of these application parameters is reasonably straightforward to predict when designing a sealing solution. However, when you compound a number of these factors (whilst often pushing some of them to their upper limit when sealing) it is crucial to predict what will happen in real application conditions. Using FEA as an iterative tool, our engineers can confidently design and then manufacture robust, reliable and cost-effective engineered sealing solutions for our customers.Starting with a 2D or 3D model of the initial design concept, produced within our advanced CAD system, we then apply the boundary conditions and constraints supplied by the customer, including pressure, force, temperatures, and any applied displacements. A suitable finite element mesh is overlaid onto the seal design, ensuring that areas of most interest have the necessary mesh size to ensure accurate results are returned for these regions whilst utilising larger mesh sizes in areas with less relevance or lower levels of displacement to minimise the computing time required to solve the model.Material properties are then assigned to the seal and hardware components. Most sealing materials are non-linear, whereby the amount they deflect under an increase in force varies depending on how large that force is, unlike the straight-line relationship for most metals and rigid plastics, at least over the displacement range relevant to sealing applications. This complicates the material model, and extends the processing time, but we use in-house tensile test facilities to accurately produce the stress-strain material models for our compounds to ensure the analysis is as representative of real-world performance as possible. What happens with the FEA data? The analysis itself can take minutes or even hours of computing time, depending on the complexity of the part and the range of operating conditions being modelled; behind the scenes in the software, many hundreds of thousands of differential equations are being solved.The results are then analysed by our experienced seal designers to identify areas where the design can be optimised to match the specific requirements of the application; such requirements may be for sealing at very low temperatures, a need to minimise friction levels with a dynamic seal, withstand very large pressures without extruding, or whatever sealing system properties are most important to the customer and the application.Results for the finalised proposal can be presented to the customer as force/temperature/stress/time plots, numerical data or animations showing how a seal behaves throughout the analysis, as appropriate to their needs, and can be used as validation data in their system design process. Project 1 case study Faced with very tight packaging constraints, a customer requested a diaphragm component from us for a valve application. Using FEA, we were able to optimise the design not only of the elastomer diaphragm itself, but also propose modifications to the customers hardware components that interfaced with it in order to increase the available space for the diaphragm, keeping material stress levels low to remove any possibility of fatigue failure of the diaphragm over the life of the valve. Project 2 case study A customer approached us to design a PTFE rotary lip seal that had to meet tight maximum torque requirements as their system was driven by a size-limited low power motor with modest levels of torque available.At the same time, high seal tightness was required as leakage of the media would have caused significant problems.By using an iterative FEA process, we produced a seal design that optimised the sealing lip geometries to provide the lowest levels of rotational friction drag whilst ensuring sufficient contact force to maintain a tight seal, and went on to provide seals that successfully passed customer validation testing.With the increased confidence in a proposed sealing solution that FEA provides, our customers can plan lower levels of physical testing and remove contingency for re-design steps, reducing their project lead times and costs, facilitating a faster and more cost-effective time to market for their new products.

Using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) in seal design 
Are all elastomers the same?Are all elastomers the same? Material hardness This is often the least considered property when selecting a material. In sealing applications, elastomer material hardness can impact assembly loads, seal friction and extrusion resistance. Softer rubber can better accommodate surface imperfections (especially when sealing low pressure gas). This means softer seal compounds can be used effectively against rough hardware surface finishes. Harder compounds will have greater wear resistance in dynamic applications.Most of the common base elastomers are produced in 60 to 80 Shore hardness range. These tend to be produced in increments of 5 hardness points. It's important to remember the hardness tolerance of a material is typically +/-5 points, therefore 70 and 80 hard nominal materials could both legitimately have a hardness of 75 Shore A.With possible hardness down to 30 Shore A (or even lower), silicone rubber lends itself to applications requiring very soft seals. An example of which is where seal compression forces need to be low to enable easy manual assembly of components. NBR, HNBR and FKM materials can be formulated up to 95 Shore A hardness for highly demanding high pressure and temperature applications; for example applications found in the Oil & Gas industry. Chemical compatibility Unlike PTFE seals (given very few chemicals that will attack and breakdown the material) elastomer seal materials must be carefully selected. This is so the properties are not affected by any fluids or gasses that the seals come into contact with. This includes the main media that the seal is retaining or excluding, additionally any contaminants (such as cleaning fluids or bi-products of reactions between any of these fluids, the seal material or the surrounding hardware).Even a seemingly straightforward application often involves a long list of chemicals and compatibility must be checked with the elastomer. Most seal suppliers publish compatibility tables or like us, have interactive tools to help check this. Even then, it’s often not the brand name oil that’s listed. For example, often at the more basic chemical level, so some knowledge of what’s actually in the fluid is required. Recent developments in health, safety and environmental requirements have made this a little easier. However, some fluid manufacturers can still be a little reluctant to declare the full list of chemicals in their products.Manufacturers sometimes give guidance on general compatibility with elastomer groups, but this can be a little generic. Additionally, not all grades in a specific group will have the same resistance to a particular fluid. Again, this can be especially relevant to NBRs and HNBRs with a variable ACN content. Sometimes the reactions can be dramatic and swift, with the rubber shrinking or swelling in a matter of hours when exposed to a non-compatible fluid and especially at elevated temperatures where the chemical reaction is accelerated. Reactions in chemicals In other cases, the reaction could be slower, but still causes sealing issues resulting in earlier system failure compared to using more capable elastomers. This is often the case with FFKM seals in applications where the cost of replacement or downtime is very high. The outstanding chemical resistance of these materials gives considerably longer service life compared to lesser grades, and it justifies the higher initial cost of the seal. In other cases, some reactions can be beneficial, for example where a small amount of elastomer seal swell in an oil over time can help to offset wear in dynamic O-ring energized PTFE slipper seals. Temperature range Outwardly, this material property seems straightforward, but elastomer technology is rarely that cooperative. All elastomer compounds will have a low temperature property stated on their datasheet. Either the TR10 (temperature at which a stretched and frozen sample recovers by 10% of its length) or the Tg (the glass transition temperature, at which all flexibility is fully lost).However, applied pressure increases the Tg by approximately 1°C for every 5 MPa. This is significant for even moderately high-pressure applications. Additionally, the flexibility required for successful sealing will vary between applications, making the correct material selection critical. At the other end of the spectrum, elastomers respond poorly when exposed to temperatures above their capability. This results in the material suffering irreversible degradation that reduces seal performance.Whilst guidance is given on maximum temperature capability for any specific elastomer grade, this is often in a benign air environment. Therefore the chemical impact of being exposed to hot fluids in the sealing application should be considered.Material groups tend to have well published temperature ranges. For example, the silicone family is able to reach -100°C (or even lower with special grades), and perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) grades are able to withstand 320°C (or even higher for short durations).Confusingly though, considerable variations can exist even within the same material families; especially with FKM where the more modern grades can now reach down to -50°C, with older technology grades only capable of -15°C. There are many NBR and HNBR grades where the acrylonitrile (ACN) content can be varied so that the low temperature limits can be between -30°C and -60°C, depending on the specific recipe formulation.This is just a short summary of three properties of elastomer materials. It’s clear that selecting the correct grade of material for a specific application is a difficult task, yet one that is absolutely critical to achieving the seal performance and lifetime required.

Are all elastomers the same? 
The importance of engineering tolerancesThe importance of engineering tolerances What tolerances are we concerned with?
We can start with the seal itself, and specifically the seal material, as almost all polymer seal materials contain multiple ingredients. For PTFE and polyurethanes this is typically 2 or 3 different elements. However, for an elastomer material as many as 30 different ingredients can be used in the recipe. Each ingredient is weighed or measured before being added to the mixing machine, with a tolerance on the mass or volume of the solid or liquid ingredient. Digital advances in weighing and dosing equipment have improved tolerance ranges since synthetic rubbers were first commercially produced in the 1930’s. However, it’s important to remember that a small variation in material mix from batch to batch is inevitable. The mixing process (also now digitised to help reduce variation) is controlled by parameters which also have a tolerance. Pressures, temperatures, speeds and times are kept within certain limits and determined by the sophistication of the mixer and its control systems. To produce the finished seal, mould tools for polyurethane and elastomer seals are manufactured using CNC or electrical discharge machining techniques. These hold incredibly tight tolerances on the metal form. However, are will be variations in moulding pressure and temperature, combined with slight variations in material shrinkage rates. This results in tolerances on the finished parts that are significantly wider than the metal tool it was produced from. For machined seals, polymer seal materials tend to have high rates of thermal expansion. Together with their relative softness makes it difficult to maintain the same level of tolerance that can be achieved when machining metal components.
Hardware tolerances
When designing hardware for seal installation, tolerances are perhaps more obvious, and certainly where engineers can focus some attention. Plastic housings (whether injection moulded or machined), together with metal castings or pressings can pose tolerance challenges. Even for relatively straightforward machined metal housings, selecting the correct tolerance to apply is key. For many applications, a stack-up of tolerances is to be considered. This is together with tolerances of the assembly such as concentricity or misalignment (especially for dynamic sealing applications). Other considerations include bearing wear and the resulting increase in misalignment or runout as the equipment approaches the end of its target life.
Why are tolerances important for sealing systems?
A combination of theory and experience over decades, seal designers have developed an ideal set of installation conditions for many applications. From static flange or face sealing, through linear hydraulic cylinder seals and to rotary shaft sealing and more. Some of these applications have adopted standardised recommendations (such as ISO 3601 for O-rings and DIN 3760 for elastomer shaft seals). However, because no two applications are truly identical, many are based on the experience and preferences of the seal designer. Regardless, every application starts from a nominal condition, and the maximum and minimum tolerance conditions should always be considered. This is even in seemingly straightforward applications to ensure the seal is continuing to operate within it’s ideal set of conditions. Sometimes it’s assumed that tolerances only really come into play when looking at very small applications, with so-called “micro O-rings”.
This is not the case - and we can illustrate this with a hypothetical application:
A device containing a 25 mm rod, static, with an FKM O-ring sealing gas, whilst installed for 10 years untouched in the Arctic circle. However, it also needs to seal oil whilst installed in direct sun at the equator for 10 years, but with the rod removed and re-fitted several times a year. The device designer would prefer not to make two different variants. O-ring calculators working to ISO 3601 would recommend a 25.12 mm x 1. 78 mm O-ring fitted in a 27.8mm groove with f7 tolerance on the rod and H9 on the groove. However, in the cold application the worst-case squeeze is looking a little light to ensure long term gas sealing. Whilst in the high temperature location, the compression and groove fill are reaching levels that could accelerate compression set of the material and cause issues when the rod is disturbed and re-fitted. Moving the nominal sizes would help one installation but adversely impact the other. However, by tightening the tolerance on the rod and the groove, the concerns at the extreme conditions can be lessened. Approaching the seal supplier for tighter tolerance O-rings can improve the robustness of the design even further, as could incorporating a custom bonded seal-rod component which would remove one dimension and its tolerance completely. Such a hypothetical application rarely exists of course, but the approach is applicable to a surprisingly large number of applications which appear “standard” at first glance. What hardware tolerances should be specified?
There is not a definitive answer to this question, but more of a recommendation that the tolerances for each component within an application are considered. Both the technical and financial impacts being evaluated. Sometimes applying a tighter tolerance can be achieved without any cost implications. In other cases it might slow the manufacturing process, or potentially require a different and more costly process (for example, grinding a rod in place of turning). Tolerances should be evaluated by the consequences of the complete sealing system not performing as intended at the absolute extremes of potential tolerance conditions. In applications where the impact of non-optimal performance may be less severe, a paper based, or theoretical tolerance evaluation is carried out. This could provide enough confidence the risk and impact of the problem arising is acceptable compared to the costs of preventing the risk further. In some safety critical applications in Life Sciences & Medical, Aerospace or Vehicle Control systems markets, testing of parts at the most extreme sizes may be required. This is to be certain that any combination of components from anywhere within their minimum or maximum range of tolerance sizes would still produce an assembly product which performs successfully in the application.

The importance of engineering tolerances 
Elastomer manufacturing moulding processesElastomer manufacturing moulding processes Compression moulding This is the simplest method of converting a piece of rubber into a finished seal product. The rubber compound is first mixed and prepared, and depending on the recipe can require up to 30 different individual ingredients. At this stage the curing (or vulcanization) of the rubber hasn’t yet taken place, therefore, the material has a stiff and non-elastic consistency (a little like thick dough). From this dough we produce a rubber blank (also known as a pre-form) by either cutting, punching or extruding cord. These blanks are normally a little bigger than the finished part (normally based on weight) and are placed into a metal moulding tool. The tool (in its simple form) is in two halves with the final product shape cut into the metal. This is known as the mould cavity.This “sandwich” of the bottom tool/rubber blank/top tool is placed into a hydraulic compression press with heated platens. This transfers the heat into the rubber via the metal tool. The press closes. The rubber is then squeezed into every part of the cavity, and any extra material that extrudes from the mould join becomes become overflow, or flash. Next comes curing of the material. This takes place through a chemical reaction between the ingredients, and is controlled by pressure, temperature and time. These parameters are pre-set according to the recipe of the material and the curing system. At the end of the specified cure time, the press is opened. The tool is then removed and split apart, and the cured (elastic) component is removed. Through a variety of methods, the excess flash is then detached, and the part may undergo a post-cure process. This fully completes the vulcanization reaction. Finally, the rubber seal is inspected, packaged and ready for application. The compression moulding process Compression moulding is sometimes a relatively slow and labour-intensive process. Some tools will have multiple cavities into the hundreds and use presses ranging in size and capacity from 20 tons to over 500 tons. This will increase throughput of seals, but the key limiting factor is the speed of heat transfer from the platens into the rubber via the mould tool. In-press cure times can be measured in minutes, but for large parts sometimes over 10 minutes or more. Removing the parts and loading the next set of rubber blanks can also be time consuming.Compression tools are quick and easy to produce, and changeover times from one component to another can be rapid. As a result, this manufacturing method is ideally suited to parts that are required in low quantities, or as prototypes. The tools are designed to ensure that the split/flash line is not located on a sealing contact surface. Therefore, high-quality parts will be produced.For some very hard rubber compounds that do not flow readily, compression moulding is sometimes the only manufacturing option. Injection moulding This is the simplest method of converting a piece of rubber into a finished seal product. First, the rubber compound is mixed and prepared. Depending on the recipe, there can be up to 30 different individual ingredients. At this stage, the curing (or vulcanization) of the rubber hasn’t yet taken place. Therefore, the material has a stiff and non-elastic consistency (a little like thick dough). From this dough we produce a rubber blank (also known as a pre-form) by either cutting, punching or extruding cord. These blanks are normally a little bigger than the finished part (normally based on weight) and are placed into a metal moulding tool. The tool (in its simple form) is in two halves with the final product shape cut into the metal. This is known as the mould cavity.Elastomer materials need to be specifically formulated for injection moulding to give them the required flow characteristics. The tooling is also significantly more complex compared to compression or transfer tools, especially with multi-cavity tools and cold runner blocks to reduce the waste in the sprue and runner system. Set-up times somewhat longer. Machinery In terms of machinery, injection presses are also more complex and costly than hydraulic compression presses, but the injection moulding process can be highly automated. This, in conjunction with fast cycle times can result in very attractive manufacturing costs for parts produced in high volumes. As with the transfer process, the flow of the rubber into the cavity can be designed to reduce the risk of air trapping and give consistent material properties in the finished part. Transfer moulding This is a variation on compression moulding. It uses the same hydraulic compression presses, but this tooling is a little more sophisticated (and consequently a little more expensive).Rather than loading the rubber blank direct into the cavity it’s held in a “well”, and the top tool part contains a plunger which squeezes the rubber though feed ports/gates into the cavity below. By using this approach, the cavity is closed before the rubber enters. This reduces the amount of flash left remaining on the part, and allows accurate positioning of metal or plastic inserts for two-part bonded components.The material may need to be specifically formulated to allow it to flow through the feed gates. The result can be a more uniform part using this flow of rubber, compared to a compression moulded part where some of the rubber has not had to flow very far during the tool closure. The part and tool can be designed so that the direction of this flow acts to expel the air from the tool and prevent it becoming trapped by the rubber in the middle of the part (which can sometimes be an issue with compression moulding).Tolerances, accuracy and consistency are improved compared to compression moulded parts but the cycle time, or throughput, is broadly the same.There are other ways to manufacture rubber parts, including extrusion, calendaring and even 3D printing, but from comparing the three most common methods of producing an elastomer seal, we can see that considering how the part is going to be made at the start of the project is key to ensuring the technical and commercial success of the seal in the application.

Elastomer manufacturing moulding processes 
Polyurethane as a seal materialPolyurethane as a seal material The foam in your armchair. The strap on your wristwatch. The wheels on a supermarket shopping trolley and beyond; Polyurethane certainly has a diverse range of uses since its invention almost 85 years ago. Aside from day-to-day products; it is also a highly capable and versatile sealing material - and an option that is often overlooked.
Here we explore a little deeper into the properties of polyurethane. Covering it's uses as a seal material and how it is manufactured. What is polyurethane?Is it rubber? Is it plastic? Rigid or flexible? The answer to all of those questions is – yes, it is all of these things! Polyurethane covers a group of materials; plastic polymers produced by the combination (or synthesis) of di-isocyanates with polyols and a chain extender.Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) belongs to the Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) family. It was originally invented by Otto Bayer in 1937 and further developed during WWII as an alternative to rubber (which was difficult to source at the time). It can be formulated to produce different finished materials with an array of properties suitable for a wide range of applications. Where do we use polyurethane? In addition to seals, polyurethane is the basis of a diversity of products. These include varnish, foam mattresses, roller skate wheels and surfboards. There are literally hundreds of different types of polyurethanes, each made in a slightly different way to suit the demands of the final product. How are polyurethane materials manufactured? In a one-step process, the polyol (a compound containing multiple hydroxyl groups) is mixed with isocyanate (highly reactive low molecular weight chemicals) and a chain extender (low molecular weight diols or diamines). The result is a random copolymer with a physically cross-linked irregular molecular structure.In a two-step process, the polyol and isocyanate are mixed first to produce a pre-polymer. This is then mixed with the chain extender to produce a block copolymer with more regular molecular structure. This can result in improved and more consistent material properties in exchange for a slightly higher production cost.We use rigid polyurethanes for sealing products. The mixed liquid material is either cast into tubes from which seals can be machined on CNC lathes. Alternatively cast into bricks which are then chipped, mixed with dye (or other additives), and fed into injection moulding machines. Why is polyurethane a good seal material?When formulated appropriately, polyurethane yields an impressive set of material properties that make it an ideal material for sealing products. It can be flexible which allows seals to be assembled into closed grooves. This capability also resists large deformation and makes them robust to survive without damage. In this respect it outperforms PTFE and is at least on a par with rubber.Polyurethane has excellent elastic behaviour, recovering almost instantly from deformation. Again, outperforming PTFE (no springs or rubber energisers needed to give the initial sealing contact stress) and matching rubber materials. However, unlike rubber it has a lower coefficient of friction, with very high abrasion resistance, tensile strength and stiffness. These properties mean it is often used without anti-extrusion/back-up rings at considerably higher pressures than even a 90-durometer elastomer O-ring would be capable of. How does polyurethane perform in tests? In abrasion tests, polyurethane has a quarter of the wear rates shown by typical rubber sealing materials. These include NBR (and considerably lower than even filled grades of PTFE). Its tensile and tear strengths are typically 3-5 times higher than rubber seal materials. Although it lacks the chemical resistance and temperature capability of PTFE, it is compatible with mineral oils.Polyurethane seal materials typically have a general operating temperature range of around -35°C to +110°C. However, more specialist grades can remain flexible down to -50°C, and other grades can push the upper limit to around 130°C.Because it can be injection moulded as well as machined from tubes, it lends itself to production of seals in both high and low quantities. This allows commercial flexibility at both prototype and production stages of a project.With complex chemistry, care must be taken to ensure sealing fluid resistance and temperature capabilities are always considered (as is the case when selecting any seal material). However, in many applications, polyurethane can often bring physical property and whole-life cost advantages over rubber or PTFE options. This can mean it bridges the gap in capabilities between these material groups.

Polyurethane as a seal material 
Diaphragms for precise control in critical applicationsDiaphragms for precise control in critical applications In applications that require precise and rapid pressure responses, our diaphragms offer an engineered sealing solution for high performance valves and actuators. Why use diaphragms? Diaphragms provide excellent sealing results in multiple applications. These include valves, actuators, pumps, pressure & flow control, pressure switches/sensors, dispensing, metering, ventilation, and media separation applications. Valves and actuators controlling the flow of liquids or gases frequently utilise diaphragms. This is for fast responses to small pressure changes with excellent hysteresis performance.The sensitivity to signal pressure changes gives reliable valve positioning (with very low hysteresis). Additionally, successful sealing in large diameter, high pressure and long stroke applications can all be achieved with the right design. Large diameter & long stroke engineered diaphragms We have a wide selection of materials (including elastomers, fabric reinforced and thermoplastics). Our range of diaphragms are an excellent seal of choice for a variety of hydraulic and pneumatic applications.With varied manufacturing options, we produce diaphragms up to 46” diameter, and our specialist profiles include convoluted, dished and “top hat” designs in both single acting and double acting formats. Are diaphragms suitable for your application? Our team of application engineers have years of seal design experience. They use the latest developments in technology to assess each individual application, providing a complete seal design service.Our mission is achieving optimal sealing performance in an application. Additionally, we can assist with hardware design to provide the most cost-effective sealing package for our customers. Our modelling and specialist FEA technologies predict the performance of fibre & fabric reinforced materials. This allows us to optimise the tooling in key areas to produce complex geometries.Manufactured in a range of materials with industry specific approvals, our diaphragms can be used in applications across multiple industries. These include oil & gas, process control, potable water management, LPG & natural gas, life sciences and food & beverage.Find out more about our range of diaphragms HERE
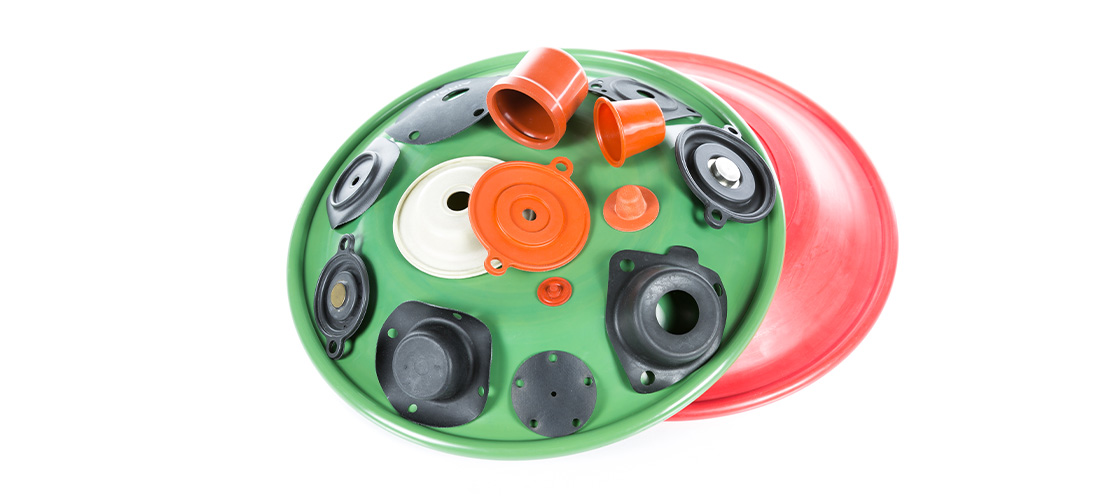

Diaphragms for precise control in critical applications 
Rotary seals for heavy duty transportationSupply Plus Ltd designs, manufactures, supplies and distributes safety and fuel delivery equipment, with brands including AS Fire & Safety, Bayley and Collins Youldon. They approached us to design a rotary seal to replace their existing solution which was causing leakage during downtime. The application Supply Plus initially approached us with a requirement for their 2” Swing joint power spindle.In this application, the outlet pipe from the fuel tank on delivery vehicles feeds into the centre of a rotating hose reel (located between the tank and cab of the vehicle). An electric motor powers the reel and pumps the fuel through at relatively low pressure.The customer’s main issue with the existing design was leakage. This is from the hose fitting in low temperatures especially at -25°C during winter, and when vehicles were parked over-night. The challenges The application required a rotary seal with low temperature capability and excellent resistance to oil-based fuels. A design was required to replace the existing seal in the available housing between the rotating metal faces. We established that a standard spring energised rotary seal would not work in the application; a bespoke design was required.The leakage at night when vehicles were not in use suggested the issue was worsened when the seal was both cold and not energised. Therefore, we designed a rotary seal that would remain energised at low temperatures and low pressure. Our sealing solution Our engineers designed a simple but effective seal. It incorporated a large heel in the base of the housing that energised a lip sealing on a rotating metal face. The volume of rubber in the heel of the seal, combined with the 170° angled base created sufficient force to maintain a seal at low pressure.We specified a low temperature Viton to ensure the seal retained elastomeric properties. It also applied the sealing force at low energising pressures and very low temperatures. This combination provides excellent resistance to fuel oils, diesel and aviation fuel. Prototypes were tested at both an in-house test unit and in the field for a period of four winter months. Results showed no issues during dispense of fuel and a complete cessation of leakage. The seal was approved and production orders placed, and now the design has been incorporated across additional sizes of hose reels.
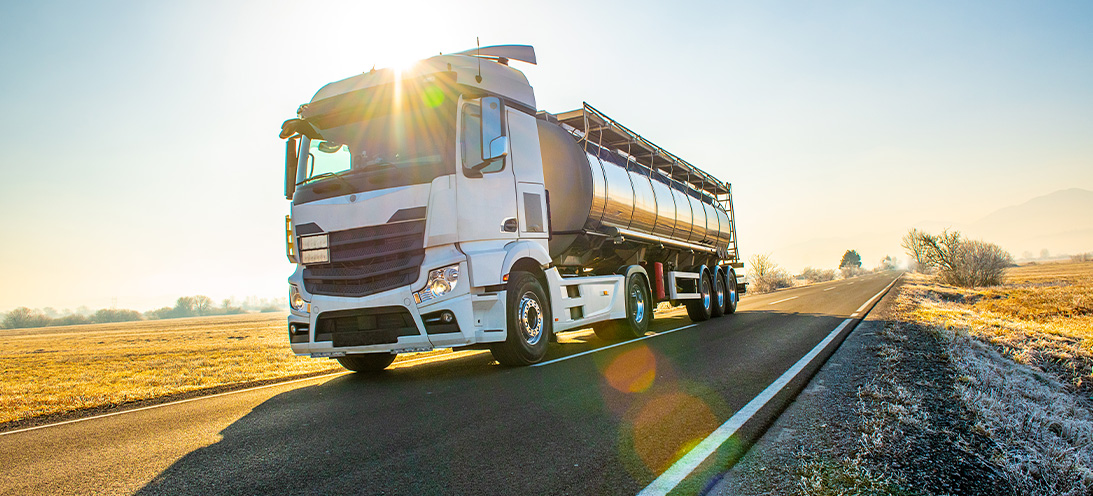

Rotary seals for heavy duty transportation 
Special coated O-rings for renewable energy applicationSpecial coated O-rings for renewable energy application Our renewable energy customer manufactures wind sensors for a variety of applications in different environments. This seal application, within ultrasonic wind sensors, is designed for wind turbine control. We explore here why special coated o-rings are needed for this application, regularly exposed to harsh conditions. The application For optimal performance, wind turbines need critical, consistent and reliable data on wind speed and wind direction measurements. Therefore, we recommended special coated o-rings for this renewable energy application.The sensors that provide this must be able to operate continuously for many years, sometimes in the harshest of weather.Operating conditions are extremely challenging because fluctuating, extreme environmental changes constantly batter the wind turbine sensors (and accompanying electronics).Depending on the location of the turbines, temperatures can range from -40°C to +90° C. Additionally, humidity changes from 0-100%, and turbines are subject to rain, hail, snow, ice, lightning, vibration, sand, corrosion and altitude. Our sealing solution For this application, the required life cycle of the sensors is10+ years. To achieve this, the electronics and sensors need a robust protective housing. This design requires a series of reliable, consistent, high-quality seals to house the electronics and sensors. These will perform without compromise in challenging conditions. Our engineers subjected the sensors to rigorous testing to confirm life cycle performance, ultimately awarding them an IPX6K rating.Each sensor size uses a set of environmental seals in the separated top and bottom sections. Together with our customer’s intensive testing program, we specified EPDM o-rings (which offer exceptional ozone resistance) with a special coating.The coatings are colour coded for identification purposes according to the size of sensor. Therefore, this creates a fool-proof assembly process with no risk of error by operators. Successfully built into nearly half of wind turbines globally, our range of seals have been cycle tested and approved by our customer.For more about our full range of o-rings, see our product page HERE
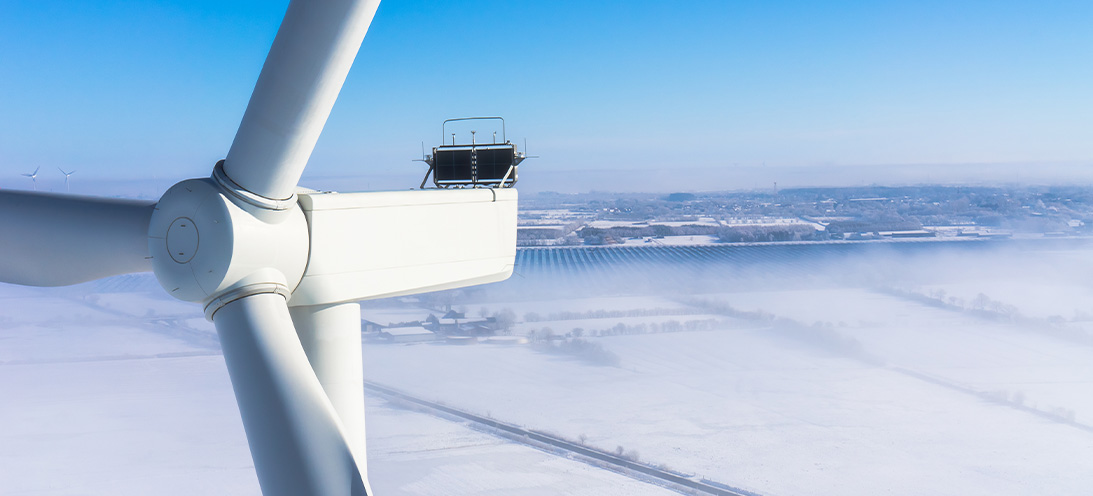

Special coated O-rings for renewable energy application 
Moulded gaskets for an automotive applicationMoulded gaskets for an automotive application An existing customer (an automotive manufacturer) approached our engineers with an application where they were experiencing failures of a seal designed and manufactured by another rubber seal provider. Here we explore more about our solution for a moulded gasket for this automotive application. The application This gasket is used within a valve housing in an automotive application. The original competitor gasket was experiencing failure at the "T-junction" areas of the seal. Therefore, our customer had experienced chronic failures of their existing design at high temperatures and high pressures.A pulsating pressure of up to 50 Bar and temperatures up to 150°C provide an extreme environment for the seal. Consequently, our engineers reviewed the existing gasket design and application conditions and recommended an increase in height of 0.40 mm.This was to increase the compression and improve the sealing function. Additional beads were also added to further stabilise the gasket in the groove. The challenges We manufactured prototype parts using a single-cavity soft tool and sent them to the customer for in-house testing and validation. The prototype gaskets nearly passed testing but fell just short of the 50 Bar pressure requirement at 150°C, achieving 42 Bar instead. Even so, they significantly improved on the performance of the customer’s original gasket.Upon analysis of customer test data and furthermore by reviewing images of the tested parts, improvements were needed. We determined there were areas where the gasket was sliding in the groove and then shearing as the pressure pulsed. To resolve this issue, our engineers added beads to the rear of the T-intersections of the gasket. This provided additional support, further stabilising the gasket at the high-pressure stress points in the groove. This reduced the amount of movement within the housing.Furthermore, the number of additional beads added needed to be balanced carefully with calculations on groove fill. Further development captured the cleanliness requirements and altered radii on the beads. Customer satisfaction With the new design approved, the customer moved to production tooling stage and sample parts were produced to PPAP Level 3. These parts have since been approved and full production quantities have been ordered manufacturing builds in 2022.For more about our mouldings & gaskets, see our dedicated page HERE.

Moulded gaskets for an automotive application 
Special O-rings for an automotive applicationSpecial O-rings for an automotive application Our customer manufactures high performance oil and vacuum pump solutions. They approached our engineers with a new O-ring for their automotive application. The application Our customer required an FKM (Viton™) 60 shore O-ring to meet Porsche material specification PN707 Class 2 (Oil), Class 5 (Fuel/FAME mix) and Class 12 (Blowby gas).This was a very cost sensitive project and the lead time required was very tight; especially as we did not have an existing grade in our materials portfolio to meet this specification. The challenges Our engineers reviewed the application, and we provided two material options. The first was a lower cost grade of FKM (Viton™) A grade. This possibly meets the Porsche specification required. The second material to be offered was a medium to higher cost FKM (Viton™) B grade. This solution determined the best fit for the specification.We supplied a quotation for both material options. These included production tooling, PPAP Level 3 submission (with samples), testing programme for both material variants and a pre-production batch of O-rings. This was an urgent project. Consequently, we could accommodate PPAP Level 3 grade O-rings for both materials to be manufactured from the same tool. Additionally, to save time we would conduct material testing in tandem with the manufacture and preparation of the production tool. The results of material testing will assist in the choice of compound used in the tool. On completion of the material testing, the customer reviewed the results with Porsche. As a result, the decision to produce O-rings from the FKM B grade was made. Customer satisfaction By this stage of testing, production tooling was complete, allowing manufacture of PPAP 3 samples and the pre-production batch to commence. Pre-production O-rings were supplied to the customer in the promised 12-week lead time together with PPAP Level 3 and PPAP 3 samples.See this link for more on our O-ring range and expertise: HERE

Special O-rings for an automotive application 
High speed Rotary seals for electric vehiclesHigh speed Rotary seals for electric vehicles The electric vehicle industry is growing; global manufacturing and registrations of electric vehicles is increasing exponentially each year. Our engineers have extensive experience in designing seals for automotive applications, but we still find new challenges involved in sealing components within hybrid, hydrogen fuel and full battery powered electric vehicles. The application Our customer has over 30 years’ experience of providing pioneering technologies globally to the mobility industry. This established company is a supplier of powertrain solutions for electric and hybrid vehicles, additionally traditional internal combustion power engines.Their team of powertrain development experts approached our engineers for a rotary shaft sealing solution for the gearbox within an electric vehicle. The position of the seal was required between the wet transmission and dry e-motor, and pressed into a bulkhead housing.The sealing lip runs on the surface of the transmission rotor shaft and pressed radially by a tension spring onto the shaft. Additionally, it required a dust lip to provide protection against environmental dirt and debris on the dry motor side.The shaft and housing dimensions were all fixed by the customer. However, they provided a full dimensional, surface finish, pressure, temperature and media specification. This enabled our engineers to review and propose a bespoke seal design Our sealing solution The application media was a synthetic oil. This is relatively standard for an automotive application. However, because of the maximum working temperature, FKM (Viton) was the elastomer material to meet the required range.As with many applications within electric vehicle gearboxes, the shaft speed was particularly high at 8500 RPM. Typically, with these high speeds, seal design needs to ensure minimal friction to ensure the service life required.Our application engineers designed a bespoke, double lipped spring energised seal.On the dry e-motor side, the rubber lip was designed to act as a dirt and dust excluder, with slight clearance from the shaft to avoid friction. This prevents damage to the seal and unnecessary wear to the rotary system as a whole.In the wet transmission side, it was imperative that the oil was kept away from the e-motor with the same minimal friction requirements. As a result, our engineers have designed the seal with an inlaid PTFE lip with 15% graphite fill. It was energised with spring to ensure force which achieves ultimate shaft sealing performance.Read more about our rotary seals HERE
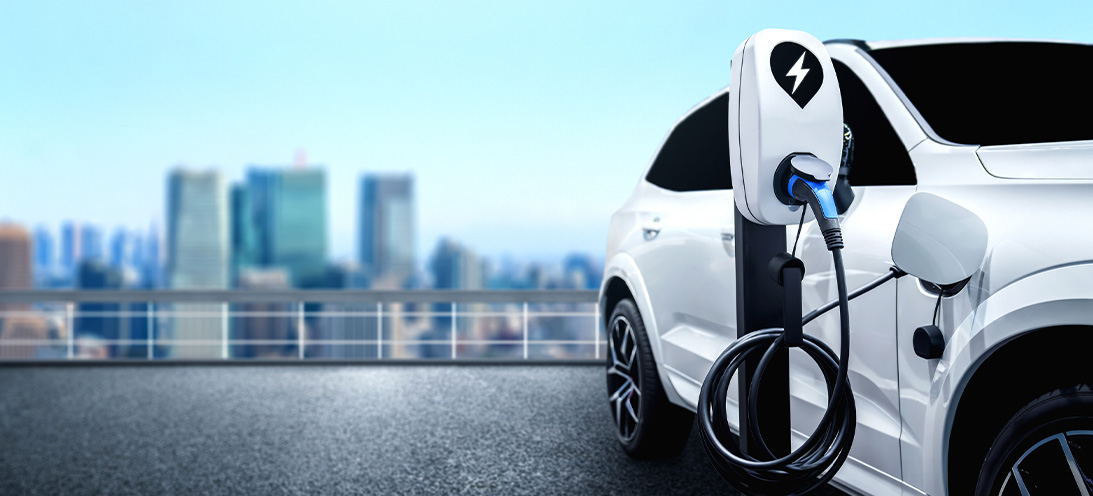

High speed Rotary seals for electric vehicles 
Silicone O-rings for De Soutter EcoPulse™ lavage systemSilicone O-rings for De Soutter EcoPulse™ lavage system De Soutter Medical Ltd specialises in the development, production and worldwide distribution of high performance orthopaedic tools for surgical procedures, offering their customers a comprehensive range of technically innovative and high quality products. The company approached us to manufacture two different sized Silicone O-rings for the ECO Pulse upgraded design. The application De Soutter Medical tasked us to support them with the pioneering new EcoPulse™ lavage system for use in orthopaedic surgery. With the brief of needing two different sized O-rings for a clinical application, our material expertise was needed. The EcoPulse™ connects onto the front of a reusable De Soutter handpiece. This allows surgeons to lavage the surgical site using saline water. It is then simultaneously connected to a suction device to remove waste from the surgical site. The EcoPulse™ is supplied as a single use sterile packed product. There are a range of nozzles available for specific surgical procedures.The new EcoPulse™ has a pared back functional design to eliminate superfluous plastic. Therefore, instead of using disposable batteries (and associated single use wiring and motors) it connects onto a reusable power tool. This tool is already being used to perform the surgical procedure.This eliminates a large amount of clinical and WEEE waste. Additionally, compared to other products in the market, reduces clinical waste by up to 60%. Our sealing solution To ensure no saline leaks, the seal application is located within the disposable pump/irrigation attachments. Additionally, it is important there is no loss of suction during use.The application was relatively straightforward in terms of mechanical sealing. However, due to the nature of the product there were critical demands on the material and during the manufacturing process.For material selection our engineers specified a USP Class VI translucent silicone. This is suitable for medical devices due to its biocompatibility features and resistance to bacterial growth.The use of release agents during the manufacture process of the O-rings is not necessary. This is due to the (bespoke and dedicated) moulding tool being coated in titanium nitride. Additionally, this is to mitigate the risk of any cross contamination with the O-rings. Eliminating risk is especially important when producing seals used within devices where there is any risk of patient fluids crossover.Cleanroom manufacturing and the O-rings are double bagged in packaging to avoid any cross contamination. These parts are manufactured and packaged at our ISO13485 approved manufacturing site to achieve these requirements. Customer satisfaction Working in conjunction with our valued customer De Soutter Medical, we assist with design support and technical recommendations on the development and manufacture of sealing products for use within their medical devices.For more on our full range of O-rings see this page: HERERead more about our Life Sciences & Medical expertise: HERE

Silicone O-rings for De Soutter EcoPulse™ lavage system 
PTFE Rotary Seal for Oil & Gas drilling toolPTFE Rotary seal for oil & gas drilling tool Our customer designs and manufactures a leading range of unique downhole technology and drilling solutions that contribute to a net zero energy industry. Read on to find out about our PTFE rotary seal solution for their application. The application Our customer tasked us with developing a sealing solution for the rod of a downhole drilling tool. This is a hydraulic dynamic (rotary) application.The normal operating pressure was 500 PSI at 60 RPM; however, maximum pressure could reach 6,500 PSI in static operation. Reverse pressure was unlikely in this application, however, the engineers wanted to ensure some level of resistance.Two single acting seals could be considered, but specifically groove space was limited. Keeping the grooves closed was preferable for bearing strength.The maximum operating temperature could reach 200°C, additionally, the application media was drilling mud and completion fluids. The wiper arrangement was already installed. Our sealing solution Because of the pressure, temperature and chemical media parameters of this application, an elastomer seal selection was not suitable. Our engineers selected our standard FTOR profile PTFE seal. This is a double acting slipper seal ideally suited to hydraulic applications and capable of sealing under alternating pressure directions. It's ideal for sealing high pressure loads with slow to moderate rotational speeds. The PTFE seal has side wall notches equally spaced, therefore the part can be fitted symmetrically either way.The initial sealing force is provided by the elastomer O-ring. This is seated within a machined saddle and activated by system pressure to perform under high pressure demands.The sealing set was also designed with a scarf cut PEEK back-up ring to ensure stability and seal performance at maximum working pressure of 6,500 PSI. Customer satisfaction Our customer tested the sealing arrangement at higher pressure (up to 10,000 PSI). They were pleased to find it sealed successfully over and above the application requirements. They have adopted this seal design for other sizes of parts in similar equipment.
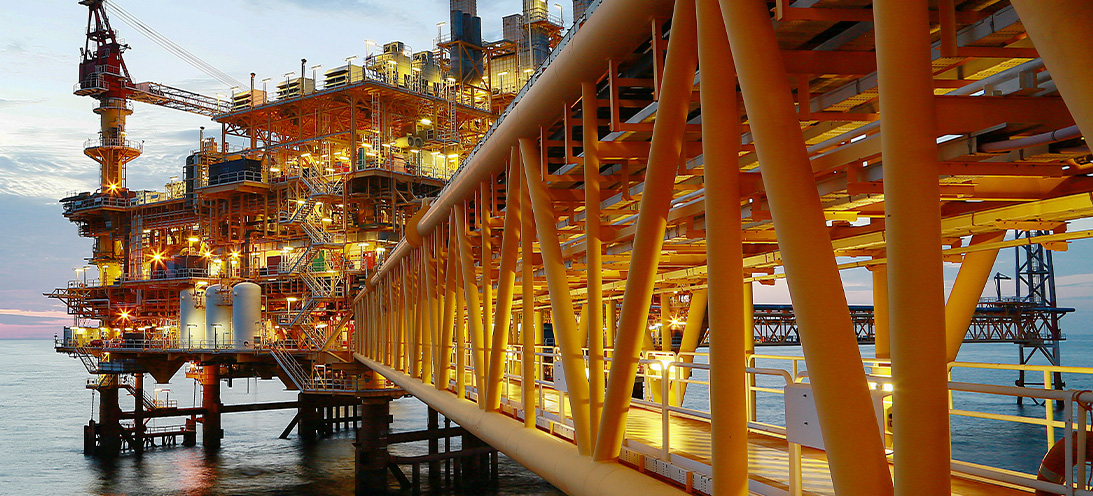

PTFE Rotary Seal for Oil & Gas drilling tool 
Why the focus on PFAS?Why the focus on PFAS? PFAS is a blanket term used to describe Poly- and Per- fluoroalkyl substances. There are currently around 10,000 substances in existence that fit this description, with potentially more variants still yet to be produced. Some are already known to be harmful to human and animal health and the environment (such as PFOA and PFOS), and these specific PFAS are already controlled under legal restrictions. But in February 2023, The European Chemical Agency (ECHA) published a regulatory proposal to further restrict the manufacture, placing on the market, and use of all PFAS within the EU. What are the consequences for seal manufacturers? A broad ban on all PFAS would have a significant and direct impact on European industries and businesses that manufacture products using these substances; and will have consequences globally.One particular concern is the fluoropolymers material group. These elastomers could be caught in any blanket ban of PFAS without any exemption.These materials are essential in a wide variety of applications in the food, medical, pharmaceutical, clean energy, semiconductor, electronics, oil & gas, chemical, automotive and electric vehicle industries.These fluoropolymers include materials used in high performance sealing solutions, such as PTFE and PVDF plastics, and FKM, FFKM and FVMQ elastomers. What's the problem? There is substantial scientific evidence to show that fluoropolymers demonstrate unique characteristics that mean they do not pose significant risk to the environment, or to human health as they’re not bio-available, toxic or mobile.They do not dissolve in or contaminate water, or generate microplastics, and as a result cannot enter or accumulate in a person’s bloodstream.They meet the criteria specified by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) as “polymers of low concern” as they present no significant toxicity concerns, and do not degrade into other PFAS chemicals.Fluoropolymers far outperform other sealing materials in countless applications. To put it simply; they seal tighter, last longer and survive harsher application environments considerably better than any other available materials. Fluoropolymers add irreplaceable value to society, and contribute significantly to environmental sustainability. What do we do? We fully support restricting the use of PFAS chemicals that are known to be harmful to our health or our environment; but we believe grouping all PFAS within a restriction would be a mistake.Fluoropolymers do not have the toxicological and environmental profiles of other PFAS, and prolonged existence alone is not justification to restrict a substance under REACH.We already work proactively to ensure the products we put to market are safe, compliant with legislation, and utilise the latest sustainability developments to minimise our impact on the environment – during manufacture, in use and at end-of-life. As a company with high environmental, social and governance standards we will continue to do so, whenever and whatever new legislation comes into force.But we believe the sealing industry, it’s many customers, end users and indeed society as a whole, need specific derogations and exemptions for fluoropolymers (free of any time limitations) to be included in any legislation covering PFAS substances.To learn more about our key industries and our sealing solutions, read HEREAs we have done, we strongly encouraged any individual or organisation that may be impacted by a ban to engage with ECHA during their consultation period on this proposed restriction (which ended on 25th September 2023).

Why the focus on PFAS? 
Seals for cryogenic applicationsSeals for cryogenic applications Cryogenic sealing means controlling or sealing a media at very low temperatures. This process can be complex and advanced, and spans a range of markets; from pharmaceutical, chemical and refrigeration, to automotive and electronics. What are low temperatures for seals? A typical industrial sealing system will operate in the realms of a stable temperature rating. This is often sufficient for elastomer seals to cope with most of the time. For example, a general pump application running at -20°C to +80°C in air or water is perfectly suitable for a sealing solution manufactured in nitrile (NBR) elastomer. However, if a temperature specification dropped to -196°C in liquid Nitrogen; the sealing solution would have to be adapted dramatically. This would be changed to a more advanced polymer sealing solution. This is because general elastomer groups such as NBR, FKM, & VMQ are simply not suitable to perform at very low temperatures. This is attributed to the chemistry of the elastomers at a molecular level.All elastomers need a particular chemical makeup to be able to withstand a temperature range of the application. However current global elastomers on the market are not rated much more below -70°C. This means elastomers are not a viable choice for cryogenic applications with temperatures below -70°C (often requirements reach -196°C or lower). Types of cryogenic sealing solutions Specialised sealing solutions are required for cryogenics conditions. Here at Ceetak, our engineers utilise a range of more advanced seal polymers to solve the most demanding and critical application setups.PTFE is often a go-to material due to its outstanding temperature rating of -260°C to +260°C and low friction characteristics. Additionally, it’s often used in conjunction with a metal spring energiser.The spring energiser acts to maximise the sealing force at the seal contact points and to maintain a tight seal. This is even when the very low temperature conditions are attempting to contract the seal away from the mating surfaces.Other common polymers suitable are UHMPWE and PTCFE for more specific applications. Our seals for cryogenic applications We offer a range of cryogenic sealing solutions for various markets and applications including; pumps, engines, couplings, cylinders and many more.Read about our full range of engineered materials HERE
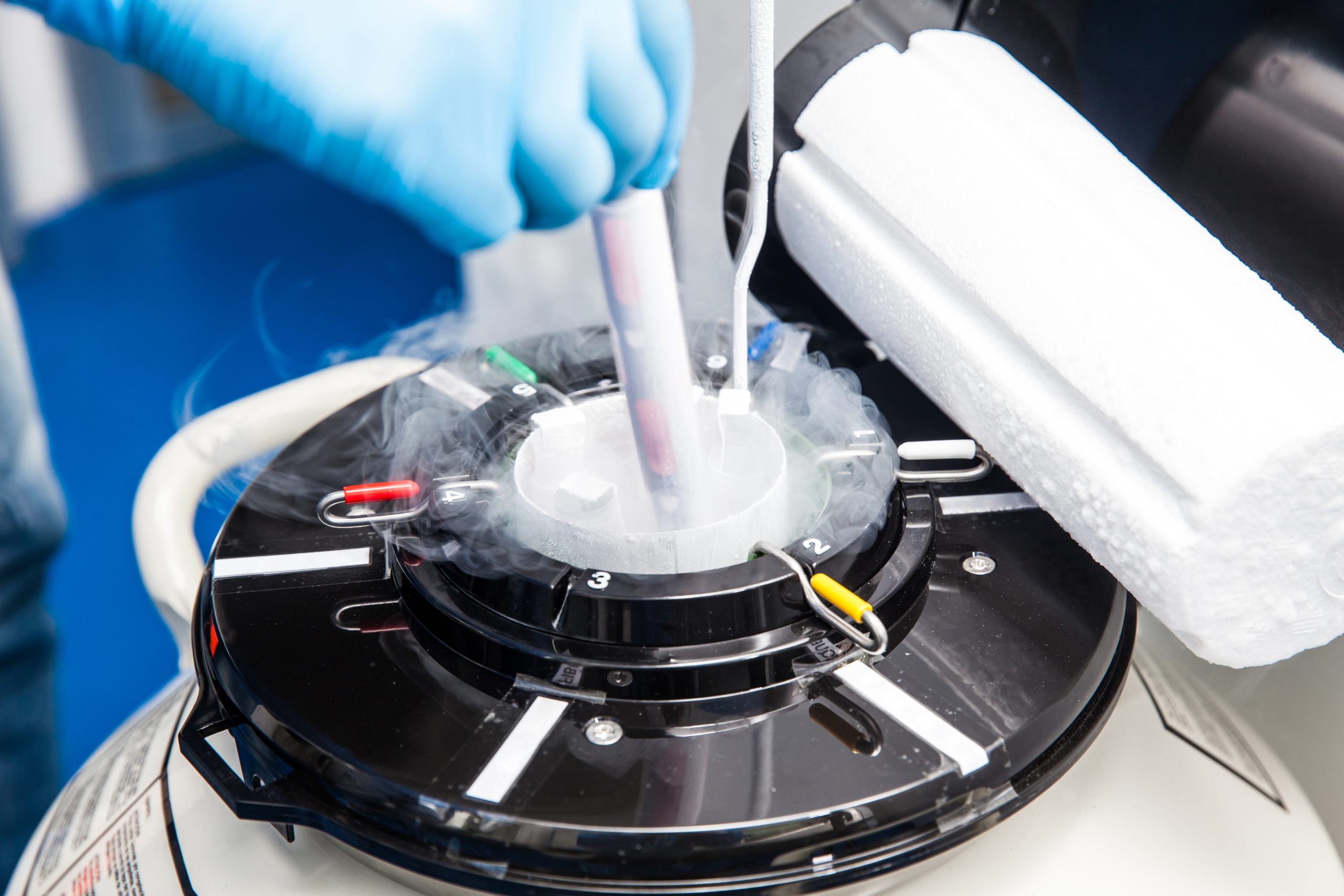
Seals for cryogenic applications 
Why use 2-Shot moulded seals?Why use 2-shot moulding? 2-Shot moulding is a manufacturing process that allows the co-polymerisation of hard (or soft) plastics and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE’s). We use the 2-Shot manufacturing approach to deliver engineered parts that perform a critical sealing function. What is 2-shot moulding? A 2-Shot mould is designed with a top and bottom cavity. During the moulding process the first material is injected into the top cavity and the mould opens and rotates. The first material is then injected into the top cavity again, while the second material is injected into the bottom cavity simultaneously. The mould then opens, and the parts are ejected from the bottom cavity. The mould rotates again and the whole process is repeated.2-Shot moulding is not considered a brand-new method of manufacturing. Actually, it has been used for years to produce items that we see and use every day. For example, toothbrushes, tools, kitchen utensils and toys are produced by multi-shot moulding. These are relatively cheap items in large production quantities. Why do we use 2-shot moulding? Previously, manufacturers of high volume metal or plastic- to- rubber component assemblies have processed them via chemical or mechanical bonding. This was by using adhesives or over-moulding. Markets that lend themselves to these types of sealing products are Automotive, Life Sciences and Aerospace & Defence.Although these production methods may achieve the final assembly requirement, the many different processes involved are lengthy, costly, and can be fraught with problem areas that require stringent controls. A failure in any of these areas will result in poor quality parts, therefore often deeming these methods unsuitable for critically engineered components. Why do we use 2-shot moulding? When designing a new 2-shot moulded product (or replacing an existing assembly part) our engineers review each application parameter carefully. They utilise years of sealing experience and materials expertise alongside the latest 3D modelling technologies. This is accompanied with FEA simulation programs -all before presenting a seal proposal. This allows us to anticipate and analyse the finest details of mould performance and means we can adjust our seal design if required. This is to ensure our customers receive the highest level of performance possible from our engineered 2-shot seal solution.The result means we supply our customers with high integrity parts with a powerful molecular bond. Additional benefits include reduced production cycle times (because additional processes are removed from the production line) and comprehensive cost reductions. This is because all parts are produced in a single manufacturing tool (meaning reduced running costs and the removal of pre and post moulding processes).2-Shot moulding is not just a way of simplifying the manufacture of multi-material parts in high volume. Our application engineers are constantly breaking norms and pushing design limits. We are proud to consider more creative ways of producing high performance engineered sealing solutions to meet our customer requirements.Read more about our 2 shot mouldings HERE
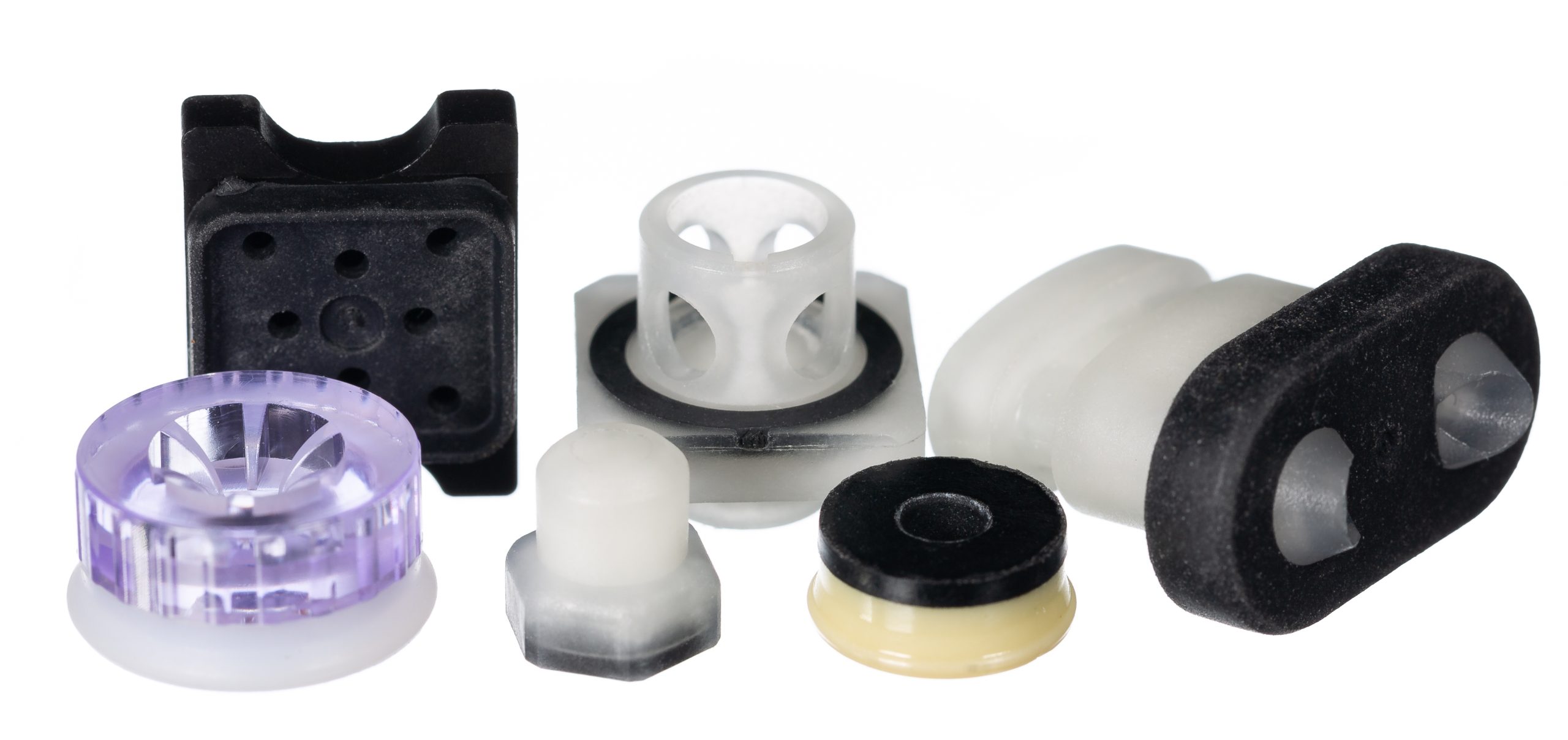

Why use 2-Shot moulded seals? 
Why use PTFE seals?Why use PTFE seals? Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a thermoplastic polymer. PTFE seals can be used in a variety of sealing applications. It’s suitable when application conditions exceed parameters of elastomeric seal use but not to the extent of a metal seal. What is PTFE? It has a high melting point (342 °C) and morphological characteristics. These allow seal components made from virgin PTFE to be used continuously at service temperatures of up to 260 °C. With the addition of fillers – up to 300°C. It has the unique ability to resist material degradation, heat-aging and alteration in its physical properties during temperature cycling. Alongside this rare combination of material characteristics, PTFE also has unlimited shelf life. Why use PTFE seals? Notably PTFE demonstrates extraordinary chemical resistance. The intrapolymer chain bond strengths preclude reactions with most chemicals, thereby making it chemically inert at elevated temperatures and pressures with virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents. Only a few media (some molten alkalis) are known to react with PTFE seals making them the perfect sealing solution for highly aggressive chemical applications.PTFE also has the lowest friction coefficient of any known solid. It has self-lubricating capabilities which offers continuous dry running ability in dynamic sealing applications and has superb stick/slip capabilities. Focus on dry coatings The advantages of using PTFE in sealing applications are multiple:Functionality at high and low temperaturesDynamic sealing with high wear capabilitiesHigh pressure sealing (using combinations of PEEK back-up rings)Compatibility with highly aggressive chemical combinations.Our range of PTFE seal products include back-up rings, rod and piston seals, slipper seals and spring energised seals in a wide variety of sizes. Materials depend on application requirements. However, we offer a wide range from Virgin PTFE or including filler combinations of MoS2, glass, carbon, carbon fibre, graphite, and bronze.These characteristics make PTFE seals perfect for the demanding applications involved in Oil & Gas, Aerospace, Automotive and Chemical Process markets (to name but a few). Ceetak’s engineering team are experienced in the design of PTFE sealing solutions to meet the complex specifications these types of application demand.Read our overview and more detail about PTFE seals HERE

Why use PTFE seals? 
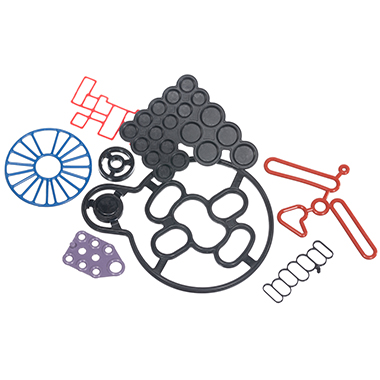
Why use Push-in-Place gaskets?Why use Push-in-Place gaskets? Where a seal groove follows an irregular path or profile, a common sealing solution is to design a custom Push-In-Place (PIP) gasket. This will have the same profile as the centre line of the groove, and simply drops into place, retained by the features of its own design. Gasket sealing overview There are many ways to seal the static join between two components. This could be to keep fluids inside a cavity, or to keep fluids or contaminants out of a device or assembly. The options will vary from simple O-rings, moulded elastomer gaskets and flat sheet style materials, to liquid gaskets (or RTV’s).As with all sealing applications, the optimal sealing solution is designed by first reviewing the application conditions. These include temperature, pressure, fluid exposure etc. Other variables such as life requirement, equipment serviceability and seal compression set will all be considered. Arguably though, compared to other sealing applications there are considerations when designing face, cover or flange sealing solutions. It is imperative to consider the packaging requirements and assembly issues of gasket sealing options. For example, if there is a need to avoid or seal around bolt holes (or other retaining/clamping devices). Additionally, consideration around optimizing hardware wall sections or depths can play an important part in choosing the most suitable gasket sealing technique. What are Push-in-Place gaskets? With the right combination of application conditions, an O-ring style approach to sealing may be the most appropriate. O-rings tend to require relatively shallow grooves compared to their cross section in one half of the assembly. In cases where the groove is round in plan view – they can be a good solution.However, in cases where the groove follows a more irregular path or profile (frequently referred to as a “racetrack”) the O-ring can sometimes pop out in places. This will be often where the two housing parts are being brought together. A common solution is designing a custom moulding with the same profile as the centre line of the racetrack groove. This will simply drop into place.A similar approach is used when the application or hardware constraints steer the design towards a gasket that has a greater cross section depth compared to the width. This would typically be designed so the centre line of the gasket matches the centre line of the groove plan profile – again so that it drops easily into place.An inherent problem with gaskets that can drop into place is that often, they easily drop out of place too. This can occur when the component needs to be inverted or has the potential for rough handling during assembly. Consequently, the gasket may become partially or fully dislodged from the groove, which results in a badly sealed interface. The best solution to this issue is to incorporate retention pips or bumps in the gasket design. This is a solution known as Push-In-Place (PIP) gaskets. These require a distinct force to put them into the groove. Subsequently, they require more than just gravity to get them out of the groove. Why use Push-in-Place gaskets? There are other less effective solutions for tricky groove sealing, such as the use of a sticky grease, or the use of an adhesive. These can bring compatibility and health and safety issues to consider. Additionally, the risk that any contaminant could keep the gasket off the surface that it’s supposed to be sealing against. As a result, the integrity of the seal can be severely compromised.Neither of these approaches can be recommended. Instead, the use of retention pips is a safe and secure way of ensuring the gasket remains in the groove. How do retention pips work on a gasket? To determine the optimum number, size and position of the retention bumps, Finite Element Analysis is used. This ensures they provide sufficient squeeze to prevent the gasket being easily dislodged. Additionally, it’s important the groove space isn’t overfilled with seal material or interfering with the seal compression footprint against the hardware faces.The bumps can be strategically positioned to control any distortion of the gasket under pressure or temperature conditions. For example, low temperature conditions can shrink the gasket and tighten the radius it adopts around a bend in the racetrack profile. This can reduce the seal compression locally and potentially create a leak path.By positioning retention bumps at either end of the bend, the thermal contraction will be controlled to minimize leakage risk.Effective retention is needed to ensure the gasket remains correctly located in the groove even with varied use. For example, if the part needs to be inverted (sometimes the preferred assembly method for practical reasons). Alternatively, it could be subject to rough handling.For large gaskets this is normally the most effective solution. On smaller gaskets (particularly those located well inside the periphery of the assembly), there is a significant risk of a dislodged gasket being totally undetected unless using a PIP gasket design. Monitoring gaskets - human eye or testing machinery It is possible to include tell-tale signs on a gasket design. For example, if a part of the elastomer gasket protrudes sideways through a gap in the housing wall the presence of the gasket can be checked. This will be either with the human eye or an automated vision system. However, this does not ensure correct seating all around the gasket length. Additionally, it cannot be used for internal gasket locations. In these cases a missing or badly fitted gasket would only be discovered during post-build testing, or even worse with a machine failure at a customer.If included at the design stage, the small additional tooling and material costs associated with a PIP gasket are negligible compared to the costs of an impossible assembly scenario, strip and re-build costs on the assembly line, or the consequential costs associated with failure of an assembly once delivered to a customer.More information on PIPs and gaskets can be found HERE
Why use Push-in-Place gaskets? 
Perfluoroelastomers in valvesPerfluoroelastomers in valves Is it time to re-visit using perfluoroelastomer seals in your valves? First developed by DuPont™ in the late 1960s, perfluoroelastomers (or FFKMs), are now widely known and understood in a variety of markets. But for those that may be less familiar with these high performance materials, here is a quick recap... What are perfluoroelastomers (FFKMs)? They are essentially highly or fully fluorinated compounds with a fluorine content above 75%. They offer outstanding chemical resistance - generally better than all other elastomer types. FFKMs are often referred to as having the resistance of PTFE but in elastomer form. The term “universal” chemical resistance is commonly used; although it’s not strictly true as we will learn shortly.Unlike PTFE, the molecular make-up of FFKM includes crosslinks (or spring-like elements). This is instead of just a backbone of carbon-carbon atoms surrounded by protective fluorine atoms. These crosslinks give the FFKMs their crucial elastic behaviour (i.e. returning quickly to their original shape after being deformed). However, the crosslinks are also a drawback as they can be a weak point for a chemical attack.Different crosslinking systems can be used when developing FFKMs and the choice will determine the high and low-temperature capabilities. Compounds developed for extreme high temperatures (up to around 325°C) generally have a less broad chemical resistance compared to the lower temperature grades (up to 225°C). Similarly, FFKMs developed to have excellent resistance to specific fluids (such as amines or high-temperature steam) can have limitations of low-temperature capability or compression set. As a result, there is no universal material that covers all application criteria bases. A variety of grades Previously, the number of perfluoroelastomer grades was less prolific than other elastomer types such as FKM, EPDM, and NBR. However, over 50 years of technical developments have created a range of FFKM grades for specific and challenging applications. These applications are particularly in chemical process, oil and gas, semiconductor, and aerospace industries. The portfolio of FFKM-based compounds available to engineers is now substantial. This is due to many options being available, which include FFKMs with a hardness range of 65 to 90 durometer. Additionally, versions that meet international standards or specifications for food, medical, CPI, and oil & gas applications also being available.In addition to technical developments, manufacturers and compounders have been addressing the only real drawback of FFKM materials; the cost. They are difficult and time-consuming base polymers to manufacture. Coupled with a relatively low volume production base and sometimes lengthy processing times for seal manufacture, FFKM seals have always carried a high financial premium over FKM seals. Even several times greater than FKM itself has over NBR.Recently, there’s been more focus on making general-purpose grade FFKMs with broader temperature and chemical resistance capabilities more financially attainable. The initial procurement costs remain high compared to less capable elastomer bases. However, the overall cost of ownership may now be more appealing than it was twenty or even ten years ago. It is possible for FFKM seals to survive for much longer in applications where exposure to a variety of fluids (perhaps wider than originally specified). This considerably reduces unplanned costs associated with maintenance and downtime. Focus on dry coatings The cost of unscheduled maintenance and repair in pump and valve equipment can be high in any industry. It is exceptionally so in petrochemical, oil & gas, and semiconductor. When these costs are fully considered in the overall lifetime of a product, the initial price of seals in a valve is considered relatively minor. However, it can still be a barrier in the material selection process.With both technical and commercial developments in recent times, FFKM materials now compare more favourably against other materials. These include static, or low-duty dynamic applications in valves. In applications where persistent and sporadic issues keep coming back to cause problems, they are now a more financially attainable choice of material to avoid re-work, overhaul, downtime, customer dissatisfaction, and ultimately, more costs.Read more about FFKM as a suitable sealing material HERE

Perfluoroelastomers in valves 
Seals for electric vehiclesSealing solutions for electric vehicles Propelled by one or more electric motors and using energy stored in rechargeable batteries, electric vehicles are quieter, have zero exhaust emissions and lower emissions in general compared to internal combustion engines. The number of electric vehicles on the road grows exponentially every year globally, and our engineers support manufacturers with innovative sealing solutions in these specialist areas of application. Hybrid vehicles Hybrid vehicles have a petrol (or diesel) engine combined with an electric motor and a relatively small battery. They feature all the traditional areas of automotive applications that require seals including oil, steering, suspension and braking systems.They also require seals for environmental and RFI/EMI (Radio Frequency Interference /Electro Magnetic Interference) applications. These are normally gaskets required for multiple electronic control, junction and connection boxes (for power invertors, charging electronics, motor and battery enclosures). These are generally placed around the vehicle; however, batteries are often under or behind the back seat. Sometimes the fuel tank is smaller, and the battery sits in a similar place.Application characteristics also include high speed rotary sealing requirements around the output shaft of the motor and potentially in the gearbox that links in with the combustion engine drivetrain. Plug-in hybrid vehicles have gaskets or seals (environmental and/or shielded) associated with the cable charging connection. Hydrogen fuel cell These vehicles have no combustion engine, and the fuel cell is often located where the petrol engine would be. Electrical power is produced by passing hydrogen and oxygen gasses through a “battery” (the cell). Anodes and cathodes in the cell produce electricity, driving the motors and is also stored in more conventional hybrid style.Waste product is water and warm air; this is very environmentally friendly. This is compared to pure battery power which uses electricity. This is often generated in a “non-green” way and which also consumes rare earth minerals such as lithium.There are traditional automotive seals in areas of applications such as steering, cooling, suspension, and braking systems. These are in addition to environmental and RFI/EMI shielding gaskets and high-speed rotary seals requirements. Hydrogen gas is normally stored in a tank at up to 700 bar pressure. Again, is usually situated just behind, or under the back seat, and requires sensors, valves and pressure regulators to operate.There are seals and gaskets required within the fuel cell itself, these require H2 resistance. Some fuel cells have small compressors which force the gasses through the fuel cell at higher pressure for improved efficiency. Then expanders which recover energy from this gas flow at the exhaust of the fuel cell. These often require high speed rotary seals (generally PTFE materials) and they run unlubricated. Battery applications Full battery electricThese vehicles have large batteries that typically take up the entire floor area underneath all of the seating compartment of a car. As with other EV’s there are the traditional seals in automotive areas; no oil system, but the steering and cooling systems, for the battery itself and the suspension and brakes. There are also environmental and EMI/RFI shielding gaskets and high speed rotary sealing requirements. The plug in charging ports also present a sealing application. Filling and chargingThere are many different applications for filling and charging. Home charging points are normally smaller and wall mounted for domestic use, while commercial and forecourt charging will encompass hydrogen filing. There are all similar application types as already mentioned including shielded and environmental gaskets for the electric applications and hydrogen sealing for the H2 filling applications. Design & Development for Electric Vehicle applications Our engineering team understand the demands associated with automotive applications, and we support vehicle manufacturers by designing innovative sealing solutions for electric vehicle applications.We use the latest in 2D/3D CAD and FEA simulation software to design and replicate automotive seal performance before finalising each individual seal design, incorporating significant feature and critical function elements for integration with customer mating parts. We offer material development and testing, and a component endurance testing service.Learn more about our expertise in the Automotive & EV industry HERE

Seals for electric vehicles 
Seals for valve applicationsSeals for valve applications Valves are imperative for isolation and control functions, and can be found in a broad range of industries such as Oil & Gas, Water & Wastewater, Food & Beverage and Hydraulics & Pneumatics. We supply seal products into valve applications in a variety of styles including ball, gate, flap, plug, butterfly, spool, check and solenoid valves. Characteristics of valve sealing There are many challenges involved in valve application sealing. Conditions and application parameters can vary with temperature extremes from cryogenic up to 325°C, and pressures up to 1000+ bar. Materials need to be carefully considered to suit all fluid compatibility required. Often the seal design requires low breakout friction and offers no stick-slip following prolonged static periods when the valve is not used. Alongside this, customers require long service life and minimal maintenance.Different valve styles include ball, gate, flap, butterfly, spool, check and solenoid valves. Additionally, different types of actuation include manual, pneumatic, hydraulic and electro-mechanical. Different areas of the valve demonstrate different sealing requirements - we explore more below. Valve sealing areas - actuation and body bonnet joint ActuationThere are a range of sealing solutions to suit the variety of actuation types employed with valves. This includes diaphragms for pneumatic actuation, rotary and linear hydraulic and pneumatic seals, and gaskets and O-rings.Seal materials are available to suit all ranges of temperatures and media associated with the actuator and any external contaminants it encounters.Body bonnet jointThis is a static sealing location that can often be sealed with an O-ring (a wide range of materials are available to satisfy fluid compatibility). However, dependent on the fluid, pressures and temperatures, metal seals may be more suited to the application. Additionally, housing deflection under pulsating system pressures may worsen compression set sealing issues. Therefore, a custom gasket design could be potentially more suitable than an O-ring. For subsea valves, a sealing solution capable of handling alternating pressure regimes and multiple media types may be required. Valve sealing areas - stem and seat body StemA critical and dynamic sealing location with often demanding requirements. Depending on the application of the valve, the seals used here may see frequent dynamic operation. They will require a long wear life, whilst in other cases, the valve may be static for long periods. It will then require operation with minimal break-out friction forces; in all cases, reliable sealing is paramount.We manufacture a range of linear and rotary seals for this location, using either elastomer or PTFE options. These include chevron sets, spring energised seals, PTFE slipper seals, wear rings and excluders. Full analysis of the valve duty cycle, internal and external medias and pressures must be considered before the optimum sealing solution can be specified.Seat body Valve seats are often mounted in a housing or carrier which has a sealed interface within the valve body. In these cases it can be a critical location to seal correctly. Dependent on the design, the seal location may be subject to upstream or downstream pressures at various points in the valve operation and in some cases fluid flow through the valve can pull or wash-out seals from their grooves if they are not designed to prevent this. As pressure conditions change with valve operation, the seals here may be required to withstand small (but sometimes frequent) movements of the carrier without sticking or wearing. We have a range of seal types and materials including spring energised PTFE and metal seals that can be used in this location (depending on the exact conditions during valve operation and use). Valve seat A wide variety of elastomers and engineered polymer materials can be moulded or machined to suit valve seat components.Bonded rubber to metal or rubber to plastic seals can provide bespoke solutions that offer benefits in terms of space envelope, component count or ease of assembly. Design & Development for valve sealing applications Our engineering team understand the application demands associated with valve sealing. We will support our customers with the design of seals for every position within the valves.Our service is a complete design process- from initial seal geometry and profile choice, to material selection and prototyping, through to final production. We utilise years of seal design experience and materials expertise. This is alongside technology such as 2D/3D CAD and FEA analysis programs to simulate performance before finalising each individual seal design.We are familiar with the requirements of individual markets and their valve applications, and offer seals manufactured in materials with approval requirements such as NORSOK M-710, ISO23936-2, NACE, WRAS and FDA.For more on our design and engineering service, see our dedicated page HERE

Seals for valve applications 
Seals for Oil & Gas applicationsSeals for Oil & Gas applications The Oil & Gas industry presents some of the most challenging demands on engineered sealing solutions. Our collaboration with Parker Seal Group allows us to integrate their materials and sealing expertise to meet our customer demands. Characteristics of oil & gas sealing The safe, dependable and efficient operation of a huge range of onshore and offshore equipment is reliant on multiple components. Seals in oil & gas applications are critical to the performance and longevity of equipment, but not without challenges. Conditions typically include low and high temperature extremes and very high-pressure conditions. Additionally, most seals need to withstand aggressive fluids and media such as sour gas, salt water and super-heated steam. There are three main sectors within the Oil & Gas industry, with different processes and equipment requiring sealing solutions.Upstream; commonly known as exploration and production – this refers to the recovery of hydrocarbon reserves in the form of natural gas and crude oil. Midstream; refers to the processes involved in the transportation and storage of natural gas and crude oil, from production site to refinery location. Downstream; includes the processing of natural gas and crude oil at oil plants and petrochemical plants. Well drilling This is the process of extracting oil and gas from beneath the ground, in both onshore and offshore environments. Seals used in these applications have to cope with increasingly harsh environments (with wells becoming deeper and deeper). System pressures up to 30,000 PSI and operating temperatures between -50°C and +220°C are common, and seals have to demonstrate excellent fluid compatibility and resistance against aggressive media – all with longer service life expectations.Applications include; drilling and tool bits, blow-out preventers, drilling mud systems, LWD and MWD test equipment, casing and pipe connections, subsea risers and connector systems, control valves, compressors and pumps.Seals need; high temperature and high pressure capabilities, sour gas and abrasive drilling fluids resistance, extrusion resistance and compatibility with well bore fluids. Well completion This is the process of making a well ready for production after drilling. Similiar to well drilling, seals used in well completion must withstand increasingly harsh condition such as deeper wells and more diverse geographical areas with extreme hot and cold weather conditions. System pressures up to 30,000 PSI and operating temperatures between -45°C and +220°C are common, and seals have to demonstrate excellent fluid compatibility and resistance against aggressive media.Applications include; tubing heads and hangars, packer assemblies, well controls, Christmas trees, cementing equipment, well head completion assemblies, well service.Seals need; high temperature and high pressure capabilities, chemical compatibility (including H2S resistance), RGD & extrusion resistance and steam resistance. Distribution Following on from the production stage, petroleum products are transported to processing facilities and to end users in pipelines. Seals used in midstream distribution sector applications often operate in low temperatures, down to -196°C (required to liquify gas) as well as high temperatures of 480°C (to meet fire test requirements). System pressures can be as high as 10,000 PSI.Applications include; marine and offshore loading swivels and turrets, railcar loading systems, pipeline service equipment (pigs and spheres), pipeline valves & actuators, pumps & compressors, tank & loading systems.Seals need; Extrusion, corrosion and abrasion resistance, extreme temperature and pressure capabilities, chemical compatibility (including H2S), RGD resistance, compliance with NORSOK, ISO and API specifications. API 6A, NORSOK M-710, ISO 23936-2 and TOTAL material qualifications The Oil & Gas industry has specific testing and qualification standards to ensure that materials used in harsh drilling and production environments meet the critical demands of these applications.ISO 23936-2:2011 describes the requirements and procedures for the qualification of elastomeric materials in accordance with media related to oil and gas production. H2S testing in accordance with this specification enables the lifetime prediction of compounds.NORSOK M-710 defines the requirements for critical non-metallic (polymer) sealing, seat and anti-extrusion ring materials for permanent subsea use. This includes well completion, christmas trees, control systems and valves as well as topside valves in critical gas systems.API 6A is the specification for drilling and production, wellhead and christmas tree equipment.Total GS EP PVV142 defines the requirements for non-metallic sealing materials concerning elastomers within pipeline valve applications.In conjunction with Parker Seals we offer a range of products in materials that are qualified to these specifications.We work closely with our oil & gas customers, read more HERE
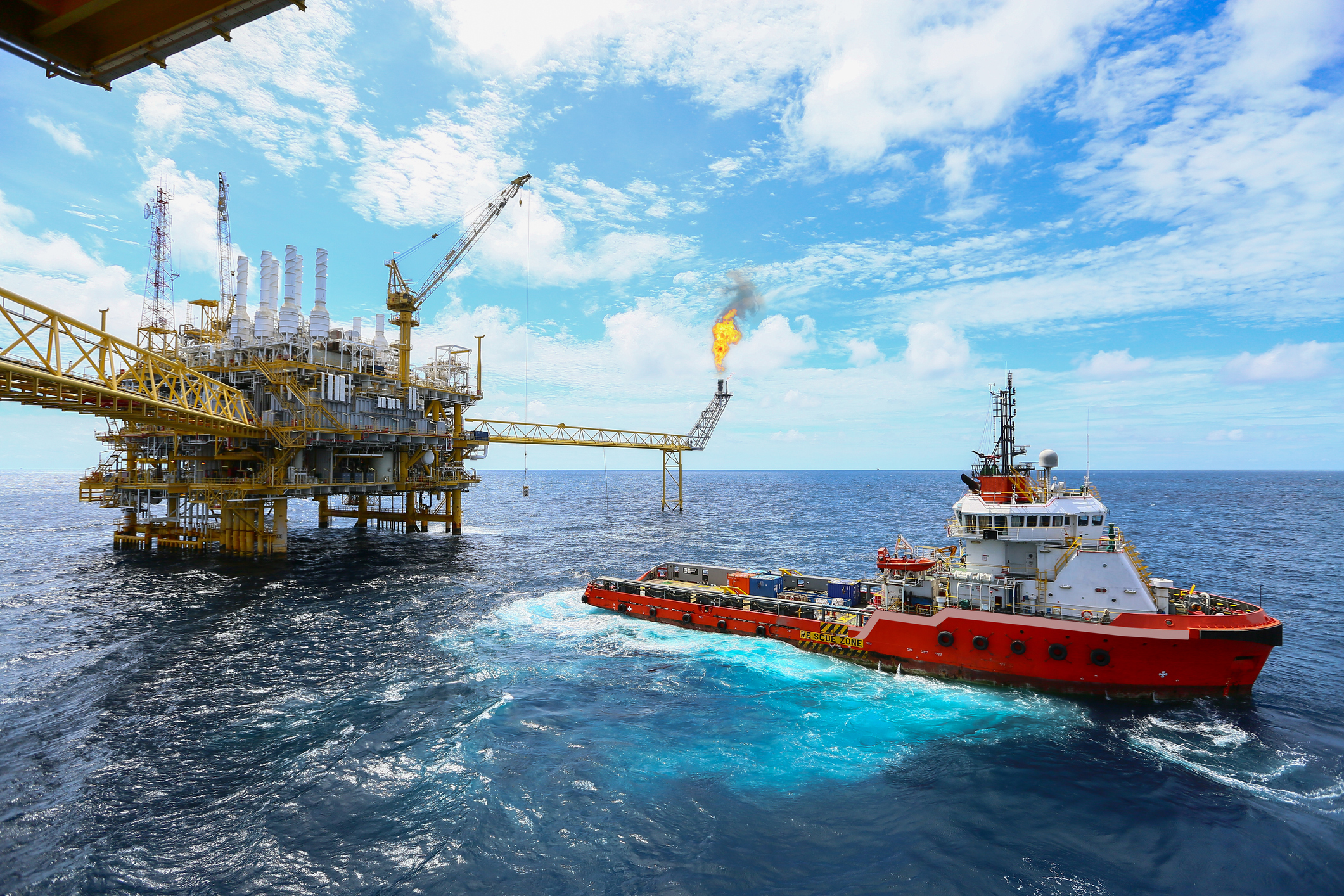

Seals for Oil & Gas applications 
Seals for Life Sciences & Medical ApplicationsSeals for Life Sciences & Medical Applications When designing and manufacturing sealing solutions for applications within critical devices and equipment, the strictest demands in product integrity and the highest specifications of hygiene and cleanliness must be met.The Life Sciences & Medical industry is one of the most demanding and stringently regulated. There are a variety of areas of product development and manufacture where seals for Life Sciences & Medical Applications are required. Diagnostics Technology changes over recent years mean there’s now many ways of supporting patients with accurate results. This means there can be safe management of health conditions; both at home and within a clinical setting. Either way, it’s vital that diagnostic devices and systems are developed with accuracy and speed of response. This is to enable targeted analysis and therapy. Typical applications include seals for in-vitro devices, analytical laboratory equipment, x-ray, and CT/MRI scanning equipment. We support your engineers with efficient design and project management of optimised sealing components for both clinical and patient self-diagnosis. Patient management and care For obvious reasons, repeatable and reliable control of the equipment used in patient management and care is paramount. Typical applications include seals for ventilators, anaesthesia pumps, respiratory therapy, monitoring equipment, minimally invasive surgery equipment and metered dose aerosols (such as inhalers). The typical demands on these types of seals include optimised working friction and wear life, critical feature’s function & tolerance control, and the management of gas, liquids, or solid media at accurate rates. Biotech and pharmaceutical processing Due to the continued development of complex and expensive drugs and research control media, the demand for high performance interactive components within the biotechnology process industry is crucial. Typical applications include seals for analytical equipment, pumps, valves & actuators, monitoring & control equipment and storage equipment & transportation vessels. We will support engineers on recommendations for Ultra High Purity (UHP) materials. This is for extreme applications combined with sensitive chemical media. Additionally to these elements, seal design recommendations for dead space and entrapment elimination within these applications. Ultra High Purity (UHP) materials Silicone based rubbers are a common choice of elastomer materials for seals used within medical devices. This is due to their biocompatibility features and resistance to bacterial growth. Commonly they're platinum cured for injection moulded liquid silicone rubbers (LSR's) and platinum and peroxide cured for compression moulded heat cured silicones (HCR's). There's a diverse range of silicone rubbers currently available in varying shore hardnesses. These are already USP Class VI or ISO 10993 approved, making them a go to choice if the specification allows.Sometimes, an application requires a seal material to have better mechanical properties, more versatility with temperature range or media compatibility. In this case, then EPDM and FKM rubbers are also a good choice.Many of our materials are fully compliant and have the required industry approvals, such as with FDA, USP Class VI, ISO 10993, UHP, BAM and BfR standards. Cleanroom manufacturing A controlled cleanroom environment is essential for manufacturing and packaging of products that must not have contact or contamination from external particulates. These include dust, dirt, airborne microbes, and aerosol particles.It’s created and maintained by removing the air. It’s then circulated through a filtering system, and the clean and filtered air is distributed back into the cleanroom environment. This can be achieved at varying levels of cleanliness. It also depends on what’s specified for each individual manufacturing environment or the finished product requirements.Different cleanliness levels are classified by the concentration of airborne particles within a measured space. We provide a complete cleanroom production process. From material blank production through to inspection and packaging using controlled materials within state-of-the-art cleanrooms.Read more about our Life Sciences & Medical industry expertise HERE

Seals for Life Sciences & Medical Applications 
Seals for Renewable Energy ApplicationsSeals for renewable energy applications Renewable energy is derived from our planet's natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, biomass and thermal energy stored in the earth’s crust. With increasing fossil fuel prices, and the very real threat of global warming and climate change to our planet; the development of renewable energy production sources is more important than everIn this article, we take a deeper look into seals for renewable energy applications and the different types of power the natural world provides. Geothermal energy and hydro power Geothermal energy is generated from heat from the sub-surface of the earth. Heat is produced by the decay of elements known as radioactive isotopes. This is a constant process in the earth’s core, and as a result temperatures reach in excess of 5,000˚C. Wells of up to a mile deep or more are drilled into underground reservoirs to tap into the geothermal resources. Steam from these reservoirs is harnessed and used to rotate turbines that activate a generator, which in turn produce electricity.There are different designs of geothermal power plants. A dry stream plant extracts steam directly from the ground and into a turbine, which drives a generator to produce electricity.The most common type are flash plants; where high pressure hot water is pumped to the surface and mixed with cooler, lower pressure water. This causes the fluid to rapidly vaporise, and the resulting steam drives a turbine.Binary power generation plants differ from the other systems. The water and steam from the geothermal reservoir never come in contact with the turbine units. A low-moderately heated geothermal fluid, and a secondary “binary” fluid (with a much lower boiling point than water) pass through a heat exchanger. The heat from the geothermal fluid causes the secondary fluid to flash to vapour. This drives the turbines to power the generator. Sealing in Geothermal applications Application conditions to consider are high temperature requirements (up to 320°C) and high pressure requirements (up to 1400 BAR).Steam is present in working turbines and drilling fluids present downhole (which may sharply change in viscosity during operational stages). Sealing drilling bores with large radial gaps is necessary.Seals are required in a range of materials to suit application needs; EPDM with steam, FKM/FFKM for high temperatures. Additionally, NBR has high expansion capabilities to seal large radial gaps. Spring energised seals offer exceptional pressure and temperature compatibility - offered in NACE approved springs (corrosion resistant). Packer elements can also assist bore alignment and offer a dense sealing arrangement which prevents cross contamination of fluids. Hydro power All forms of hydropower convert energy from water flow into electricity through the operation of a turbine and generator. There are different methods of hydropower production. Three of the main techniques are Impoundment, Diversion and Pumped Storage. Impoundment uses a dam to store river water in high reservoir. Water in the reservoir is manually released and the kinetic energy of its flow (as a result of gravity) is converted to electricity through a turbine and a generator. A diversion facility channels a portion of a flowing river through a separate channel. The channel will direct the water to a turbine and turn it before it re-enters the river at a lower point.
The principle behind a pumped storage facility is that water is pumped to a higher elevation, and then manually released back to the original lower reservoir. The energy used to originally pump the water up can be extracted by a turbine and generator for use as electricity. The idea of pumped storage is to store the energy like a battery and use this in times of demand. Sealing in hydro power applications This technology provides a range of application environments, with varying water conditions and sources.Hydro power stations contain large and heavy-duty mechanisms when dictating the flow of water. High rotational speeds will be achieved on some turbines. Wear and abrasion resistance must be considered with potential for higher load impacts from initial water release. Seals in a comprehensive range of elastomer compounds must be considered to ensure compatibility between varying water conditions. Heavy duty application rotary seal designs are suitable (in some cases with metal casings. Additionally, PTFE seals are suitable for applications that require abrasion and wear resistance. Wind energy This is the process of converting the kinetic energy of wind into electricity through a wind turbine.Most wind turbines feature three blades, and the shape of the blades are similar to the design of an aircraft wing so that the air flow around them provides lift. The force of the lift is much stronger than the wind’s force against the front side of the blade (which is called drag). The combination of lift and drag causes the rotor to spin like a propeller which in turn causes rotation of a shaft at the blades’ axis. The shaft is attached to a generator, which produces electricity from the torque of the shaft.A streamlined enclosure called the nacelle houses the key components of the turbine; including the gears, rotors, braking system and generator. There is a pitch control mechanism (comprising of hydraulic cylinders) to ensure that the blades are rotated at an angle to receive the wind and encourage lift most efficiently, and a yaw mechanism (located at the base of the nacelle) which rotates the entire body so that the front of the hub faces the direction of the wind.The shaft is incorporated into a gear system which has another higher speed shaft attached to the end. The gear box provides a gear ratio that can be up to 100:1, relative to the low-speed shaft connected to the blades. The high-speed shaft provides torque to a generator which converts this force into electricity. Application conditions Application conditions for seals can vary depending where in the turbine they are located. General environmental factors include varying weather conditions, vibration, contaminants, corrosion, altitude and diverse (and often fluctuating) temperature ranges (-40˚C to 85 ˚C). Often long life cycle and ease of installation are considered important (as downtime and maintenance are extremely costly). Areas of application are broken down below. Gearboxes, braking systems and Pitch & Yaw systems Gearboxes:There are a range of rotational shaft speeds to consider here. Typical high-speed shafts can reach approximately 2,000 RPM so require high wear resistant seals and shaft misalignment often needs to be considered. In low-speed shaft applications, contamination from outside elements must be prevented. Rotary V-Seals reduce contact pressure as RPM increases (due to centrifugal force) which allows operation at a variety of speeds and reduces the chance of heat friction/friction loss. They also offer flexible lip arrangement to compensate for shaft misalignment. Oils and grease are used to lubricate systems so multiple compounds are available for compatibility.Braking systems: A wide range of pressure requirements are seen; low working pressure until brakes are applied, and then high and uni-directional pressures activated. A range of brake fluids and oils are used so material compatibility must be considered. O-ring energised Polypak® seals, step seals and slipper seals all seal at a flexible tolerance range - offering sealing capability at low and higher pressures. PTFE seals offer a very consistent and strong chemical resistance. Scraper seals contain fluids in brake system compartments and prevent components running dry. Pitch & Yaw systemsThese present both static and dynamic sealing applications, but inconsistent dynamic operation (as it depends upon wind conditions). Both low and high pressure will be seen (for example, accumulators within pitching system present up to 250 BAR). Shaft offset/misalignment must be considered in heavy duty yaw systems. Hydraulic fluids and diverse lubricants require material compatibility choices. O-ring energised PTFE step seals will seal at a flexible tolerance range and offer sealing capability at low pressures. Engineers can design sealing assemblies, made of other products, to work together to seal against high pressures. Polypak® seals also offer sealing when high pressure is applied and when under ambient conditions. O-ring energisers and wear rings help to contain shaft run out. Seals for Renewable Energy Applications In summary, seals are a vital part of the critical function of components in renewable energy power generation. They are required to provide long term functionality and provide durability in harsh environmental conditions. Our range of engineered sealing materials are designed to withstand critical sealing characteristics in these applications, including wear resistance, high pressure and high temperature conditions.Hydrogen and renewable energy is one of our key industries. Read more HERE

Seals for Renewable Energy Applications 
Seals for Semiconductor ApplicationsSeals for semiconductor applications There are greater demands on semiconductor and electronics manufacturers for more complex and powerful devices to fulfil applications across all industry segments. High performance seals and ultra high purity elastomer materials are crucial for these critical applications. Characteristics of semiconductor sealing The technology push for more complex devices requires semiconductor companies to research and design new methods of processing within their manufacturing cells. This brings an increase in challenging technical conditions including complex chemistry, increased temperatures and stringent cleanliness within manufacturing process and the surrounding tools.Component and material suppliers face these complex challenges daily. They must follow the same rules and ensure all criteria for new processes are fully met. Suppliers must also consider the combined effects of all the conditions outlined above.Our world demands modern performance materials for the semiconductor industry. It’s therefore apparent materials previously formulated for older generation tools may not be technically capable in new and future applications. Therefore, it’s paramount to investigate and formulate new performance materials that meet each specific application.Wet cleaning and ECDWet cleaning is a method used in semiconductor manufacturing to remove any contaminants from each layer of the wafer surface, usually by using chemicals and pure water. ECD is a method of laying down the bulk of the copper wiring within a semiconductor device. Compounds for wet cleaning are engineered for static and dynamic applications with minimal metallic ion contamination.Thermal applicationsCompounds for these applications are required to have excellent thermal stability and maintain integrity at elevated temperatures often found in processes such as Oxidation, Diffusion, Annealing, and RTP.These processes are extremely challenging for seal materials. High thermal load at 300°C with temperature cycling can encourage compression set, and they must also be manufactured to limit out-gassing at high temperature to prevent contamination within the process area and offer superior physical properties. Thin film and dry etch Thin film deposition is the process of creating and depositing thin film coatings onto a substrate material. These coatings can be made of many different materials, from metals to oxides to compounds. Dry etch is a process for material removal.There are many Thin Film applications that present harsh plasma and gas environments, often at elevated temperatures. These include HDPCVD, PECVD, SACVD, PVD and ALD, along with Dry Etch and Ashing processes.Whereas traditional seals might deteriorate and fail in these conditions, our next-generation compounds have excellent chemical and thermal resistance. Consequently, they are virtually impervious to extreme fabrication processes, therefore excellent for semiconductor seals.Plasma processes are a very hostile and aggressive environment for seal materials. The corrosive chemistry at temperatures up to 250°C means compounds must be chemically and thermally stable across the operating range. Additionally, they must include low-outgassing and low particle count features. These applications are varied; from window and door seals, chamber lid seals, valve seals, and exhaust flange seals. They each require application knowledge to ensure all technical parameters are met before materials are recommended. Ultra High Purity (UHP) materials Perfluoroelastomer materialsFFKM’s contain fully fluorinated polymer chains. Subsequently, FFKM elastomers deliver ultimate performance in multiple applications. These applications include where seals encounter high temperatures and aggressive chemicals for plasma, wet and dry, semiconductor process applications. There is an extensive range of FFKM materials available. The challenge lies in selecting the correct material grade for each application because no single perfluoroelastomer can meet all semiconductor process requirements. . For example, some materials are better than others at high temperatures, some demonstrate better chemical resistance and some are poor at thermal expansion.Several compounds within our range of PERFREZ® perfluoroelastomer materials offer the best performance characteristics based on high thermal values, excellent low out-gassing and low particle count. We also offer a hybrid material which is an excellent “all-rounder” as it’s chemical formulation falls between FKM and FFKM. This means it performs consistently under slightly less demanding application conditions and with the added benefit of lower cost of purchase versus ultra-high grade FFKM’s.Other compounds within our range are very specific to semiconductor process applications such as CVD, PVD, Plasma Etch (oxide & metal), fluorine and oxygen compatibility with a high temperature threshold material for sub-fab NW /ISO exhaust line environments. As new challenging processes emerge within the semiconductor industry, further progress in high temperature materials above 300° C will be developed. We expect to add a new generation material for plasma applications to our portfolio of materials by the end of 2022. Cleanroom manufacturing Semiconductor cleanrooms must be designed to control static, out-gassing, and any contamination. This includes external particulates such as dust, dirt, airborne microbes, and aerosol particles. Just a single particle of dust or debris on a wafer or component is enough to cause a catastrophic defect (that will ultimately lead to failure of a device). Technicians create and maintain cleanrooms by removing the air and circulating it through a filtering system. The clean and filtered air back is distributed back into the cleanroom environment. Varying levels of cleanliness are possible. It depends on what is specified for each individual manufacturing environment or the finished product requirements. Different cleanliness levels are classified by the concentration of airborne particles within a measured space.Bringing in any auxiliary products (such as seals) into the environment must also maintain the same levels of cleanliness.We provide a complete cleanroom production process; from material blank production through to inspection and packaging using controlled materials within state-of-the-art cleanrooms. Our clean room manufacturing facilities are Class 7 (10,000) manufacturing and Class 5 (100) inspection, cleaning, & packaging.Read more about our expertise in the semiconductor industry and how we can help you with your seals for semiconductor applications HERE
Seals for Semiconductor Applications 
3D printing for seals3D printing for seals 3D printing has developed significantly and now performs a crucial role in many applications. 3D printed products vary from fully functional to purely aesthetic applications – commonly for manufacturing. Here we discuss how our engineers use this technology to demonstrate a seal concept. What is 3D printing? The typically common name for additive manufacturing is 3D printing. The process involves the construction of a three-dimensional shape designed and generated from a computer aided design program (or CAD). The most typical process used for 3D printing is FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) or FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling).The FDM process uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. It’s then deposited onto the 3D print bed, creating layer by layer, gradually building up the 3D model structure. We commonly use this process to create our design and development range of 3D printed models and seal prototypes. What material is suitable for 3D printing? Material compatibility with the process is imperative and a range of thermoplastic grades are used. Typical suitable material grades include; Polylactic acid (PLA), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), Nylon and Polypropylene (PP).The most common grade we use for 3D printing is PLA – for its great strength and stability. We’ve also adapted our design process to use more TPU based material grades, as it loosely demonstrates the same properties as elastomer grades and is better for using in prototype programmes where mechanical fit in groove is tested. Why use 3D printing for seals? 3D printing is used for a variety of designs and seal types. From O-rings, gaskets and lip seals – to grommets, multi shot mouldings and large seal assemblies.Using 3D printing during the initial design stages of a project comes with many benefits. The rapid turnaround means a simple seal design will be produced in around 15 minutes. Additionally, even more complicated parts can be manufactured in the same day. We can even print the application housings – a perfect demonstration to an engineer what they can expect from a seal part. They will see the shape and fit for hardware without the lead time and cost of cutting a prototype tool for moulded parts.This solution is particularly suitable for quick turnaround gasket designs. For example for automotive applications or similar critical markets. Our engineers can design the concept and then 3D print a rapid prototype of a gasket to suit a 3D printed gauge groove. Demonstrating to our customers that the seal has been fit checked for installation, builds further confidence in the design recommendation. Our engineers combine the 3D print with FEA simulation reports to offer a fully engineered sealing solution.Learn more about our design and simulation service HERE
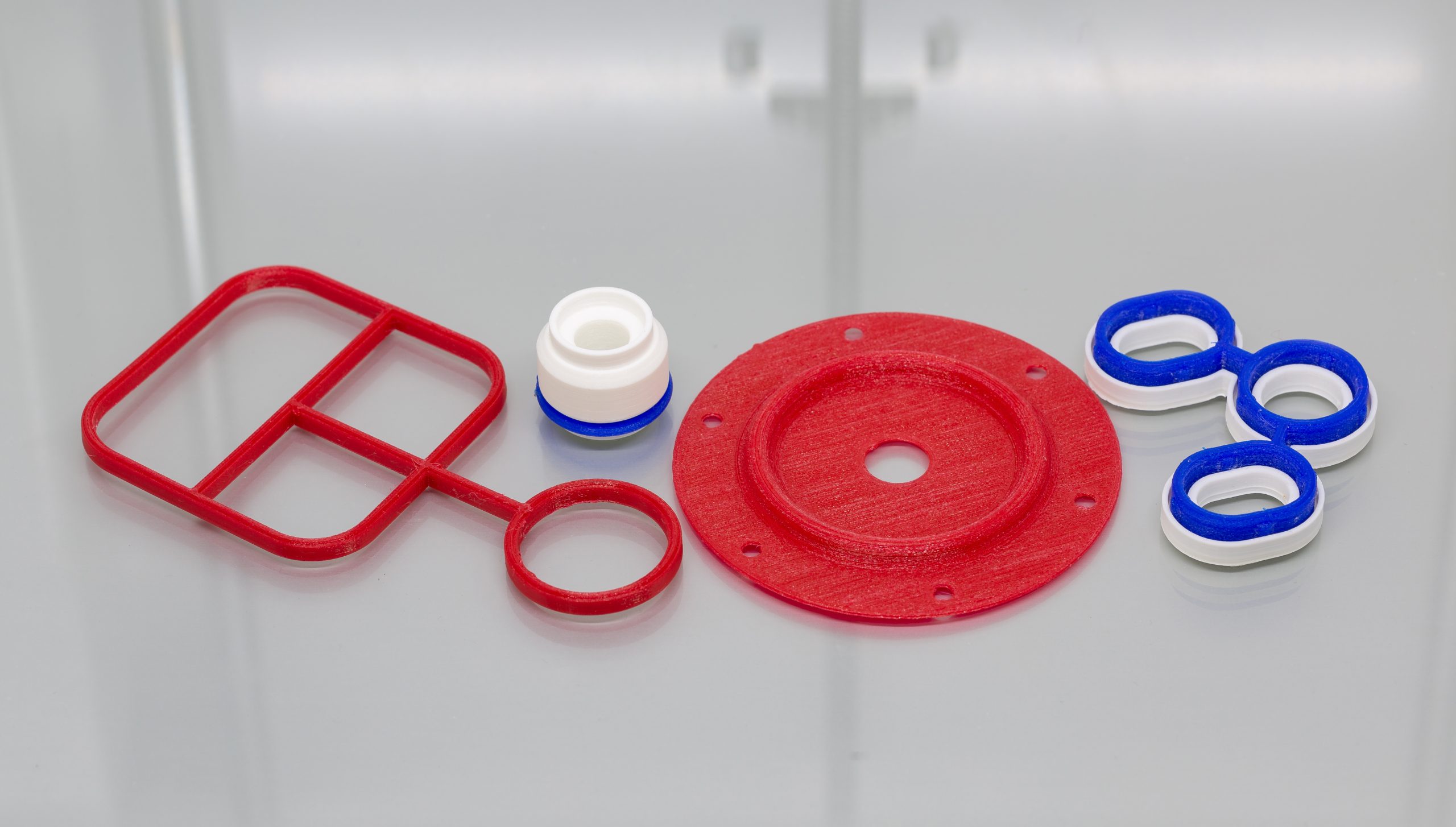
3D printing for seals 
O-rings with special coatingsO-rings with special coatings All seals require some form of installation into application hardware and often this is a simple push in place function. However, without consideration of certain conditions sealing problems could be created further into the life cycle of the seal.Once installation is achieved, a seal often sits in the housing hardware for many months. This potentially allows it to stick to the housing material and cause further issues. This is where O-rings with special coatings can make a difference. Why use special coatings for seals? The main function of coatings is to improve installation into the hardware and to lower friction within an application. Here we discover many other benefits.Coatings often mean that lower assembly forces are required. By not using grease lubricants, seal parts don’t stick together in packaging for transit.Special coatings can be manufactured in different colours. This means seals and O-rings for specific applications are easily identified without the need to reformulate the elastomer compound with colour additives. These reasons make them easier to handle for users during installation. What types of coatings are there? A variety of coatings and lubricants are available for the surface area of seals. These are mainly divided into two common categories: wet coating/lubrication or dry micro film coating.Historically, coating technology was limited to just using wet type coatings. For example, these may include silicone oils and greases and mineral oil-based greases. The coating process would involve simply dipping the seals in the oil or grease during manufacture, or during installation on site. This is often a messy process, and although a relatively low-cost method, wet coating is less common. This is because more applications demand higher levels of cleanliness and control of products, and low contamination has become a key factor.Alongside the typical wet coatings traditionally used, there is an extensive range of what is often referred to as dry coatings. Common offerings are silicone dry coating, PTFE coating, PFPE coating, special polymer coating and MoS2 dry powder coating. These are applied during the manufacturing process and bagged in a clean and efficient process, delivered and ready to be installed into application straight from the bag. Focus on dry coatings Dry coatings are fast becoming the coating of choice for many customers, with PTFE dry coating being one of the most popular. Commonly applied to O-rings, the process involves the PTFE polymer being spray applied to the O-ring elastomer surface area. This creates a microscopic thin film layer. At molecular level, the PTFE creates a covalent like bond to the surface ensure a high quality finish.The low friction properties of PTFE gives the advantage of low assembly forces. For example, an O-ring assembled to a piston can be installed easily into the bore hardware housing mating part. Consequently, this greatly reduces the chance of installation damage (like pinching of the O-ring elastomer material).PTFE coatings are also used as a short term dynamic improvement to a sealing solution, because many seals suffer from the phenomenon called stick slip. This can occur where a seal has remained in the application hardware bore for a medium to long period of time. It then starts to adhere between the surface of the elastomer and the mating metal material, causing sticking.When a PTFE coating is applied between the elastomer and the metal hardware, it creates a low friction barrier. This provides a significant advantage over uncoated parts. This is because the PTFE coating generates a low friction layer, greatly reduces breakout friction and resolves the stick slip issue therefore greatly improving the performance of the application. Coating colours for O-rings Because the PTFE is a thin polymer layer, coatings can be manufactured in a range of colours by adding pigment to the recipe. Typical colours include, green, blue, red, yellow and orange. Adding these colours means the customer benefits from easy identification and production line inspection. Furthermore, seals are more easily identified - even once installed.Find out more about our range of O-rings with special coatings and the different materials O-rings are available in HERE
O-rings with special coatings 
E1244-70 seals in Life Sciences & Medical applicationsE1244-70 seals in Life Sciences & Medical applications Packed with multiple benefits, E1244-70 recommended for seals in Life Sciences & Medical applications. Specifically suitable for pharmaceutical manufacturing, biopharmaceutical processing and disposable medical devices, E1244-70 is an internally lubricated compound. With this material, there is no need for an external lubricant. What is E1244-70? E1244-70 is a 70 durometer internally lubricated, black EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber) material. Possessing an internal lubricant, which reduces installation force and dynamic friction, E1244-70 is compatible with all water-soluble chemistries. Additionally, it has excellent resistance to repeated conditions such as steam, gamma, ozone and ethylene oxide sterilization. Adding external lubricants can be problematic due to the risk of leaking into flow paths and migrating into areas where they are not needed. Additionally, even ‘clean’ lubricants like USP silicone, which can trap dirt and dust, can compromise patient health. Removing the need for an external lubricant by using E1244-70 is clean and safe with no risk of leakage. Benefits, application and use With a temperature range of -54°C to 121°C (-65 to 250°F), E1244-70 has a low compression set, and is suitable for both dynamic and static seal applications. Because this material does not need an additional lubricant, it prevents multiple issues associated with non-lubricated seals. For example, mismanagement by not using a lubricant when needed, can lead to friction and heat build-up, resulting in erosion and potential leakage and failure of the application. The material is compliant with USP Class VI biocompatibility and USP cytotoxicity standards (for life sciences applications). The internal lubricant derives from the fatty acid family, which significantly reduces patient reactions. This means it is safe for medical devices and pharmaceutical applications. In summary, it is suitable for:Dynamic applications & difficult installationsSurgical instrumentsPharmaceutical manufacturingBiopharmaceutical processingDisposable medical devicesRepeated device sterilization Our Life Sciences & Medical expertise We have clean room manufacturing facilities which are Class 7 (10,000) manufacturing and Class 5 (100) inspection, cleaning, and packaging.Our application engineers utilise the latest in 2D/3D CAD and FEA simulation software to design and replicate seal performance. This is before finalising each individual seal design, incorporating significant feature and critical function elements for integration with customer mating parts.We offer material development and testing, and a component endurance testing service.Learn more about how we support our customers in the Life Science and Medical Industries HERE

E1244-70 seals in Life Sciences & Medical applications 
Seals for Hydrogen ApplicationsSeals for hydrogen applications Hydrogen is the most common element in our universe, and is becoming an increasingly vital part in decarbonisation and a global sustainable energy future for our planet. How is hydrogen produced? Hydrogen offers a clean energy solution to parts of the economy that are difficult to decarbonise. These include industrial processes, domestic and industrial heating, and hard-to-electrify transport. This includes heavy-duty vehicles, ships and aircraft (where battery solutions are much less practical than they are for passenger cars). Hydrocarbons and water lock away most natural hydrogen, making it difficult to obtain.Extracting hydrogen from either of these sources takes energy (and a lot of it!) but hydrogen becomes emission-free at the point of use. Today, 96% of the world’s hydrogen is produced using grey and brown processes. This means it’s not very environmentally friendly at all. It is widely accepted that we need to switch to, and expand green hydrogen production. However, the electricity sources for green hydrogen (solar, wind, etc) are not always located where the hydrogen needs to be used - and cannot be turned on and off as energy demand fluctuates. The different colours of hydrogen Generally categorised by a different colour, hydrogen is obtained by a variety of different methods. Grey hydrogen is produced by reforming natural gas (methane). Brown hydrogen is produced by converting carbon rich materials (such as coal) into hydrogen and carbon dioxide. These are common processes, but result in substantial carbon emissions. Turquoise hydrogen is produced by the pyrolysis of methane at temperatures over 1000°C. Solid carbon is a by-product which is used or buried without emitting greenhouse gases or causing groundwater pollution. Blue hydrogen is generated by the steam methane reforming of natural gas. This generates large amounts of CO2 which must then be captured and safely stored. Pink hydrogen is created where large amounts of electricity is used to chemically split water into hydrogen and oxygen. Manufactured from a nuclear power plant, it’s free from ongoing emissions (other than those emissions produced in building the nuclear power station). The oxygen can be used by industry or vented to the atmosphere, without harming the environment. Green hydrogen is also produced by electrolysis of water, but the electricity required is taken purely from renewable sources such as solar, wind, tidal and geothermal processes. Experts widely regard this process as the only truly clean method of hydrogen extraction. Engineered seals for hydrogen applications Sealing hydrogen presents several challenges and we need to consider the following parameters when designing a sealing solution.When it’s a gas, we need to consider the gas permeability of the sealing materials with pressures of 700 bar or more. The tightness of the static or dynamic sealing surfaces – including surface finish requirements for the mating components, also needs consideration. As a compressed and cooled gas, pressures can be up to 1000 bar in conjunction with temperatures down to -240°C. When it’s a liquid, the sealing solution needs to be suitable for the associated cryogenic temperatures of -253°C. However, pressure regimes are generally less than 5 bar in these conditions.When hydrogen is within a carrier, the chemical compatibility requirements of the carrier medium must match the sealing materials specified. Carries include ammonia or liquid organic hydrogen.Electrical conductivity or resistivity requirements, together with cleanliness and purity, may be required for sealing materials used in electrolysers and fuel cells.Chemical and temperature compatibility with all the media associated with hydrogen production, transport and conversion processes, including all by-products, emissions, cooling fluids and electrolyte materials. Seal applications in hydrogen For seal applications in hydrogen with no particularly high demands in any one area, EPDM elastomer based solutions can often be the most cost effective. We offer chlorobutyl elastomer or polyurethane seals for permeation resistance. In high-pressure applications, engineers use elastomers or polyurethanes resistant to extrusion and rapid gas decompression, or PTFE unaffected by RGD.In electrolysers and fuel cells, the purity and cleanliness requirements can be met with materials and treatments we frequently use within the semiconductor market. For applications below -60°C, elastomers become hard and brittle, but PTFE, PCTFE and metal sealing solutions can be used down to cryogenic temperatures. For high temperature applications, some FKM or even FFKM elastomers are used up to 220°C or even 300°C. However, the normal preference here is PTFE sealing solutions.Metal seals are capable of even higher temperatures up to around 870°C. Metal seals can also have soft coatings such as tin or indium to achieve gas tight sealing, or gold or silver to reduce the risk of hydrogen embrittlement. The evolving hydrogen industry The hydrogen industry is technically vast and challenging for sealing applications, covering both extremes of temperature, alongside demanding pressure and chemical resistance requirements, coupled with stringent leakage limits and associated safety requirements.Applications typically demand long service life and in certain cases require parts with high levels of technical cleanliness and purity.Full consideration for the application is imperative. Elastomer, polyurethane, PTFE and metal sealing solutions are all options - providing the design and environment work harmoniously together. Learn more about how we serve customers in the Hydrogen & Renewable Energy Industry HERE

Seals for Hydrogen Applications